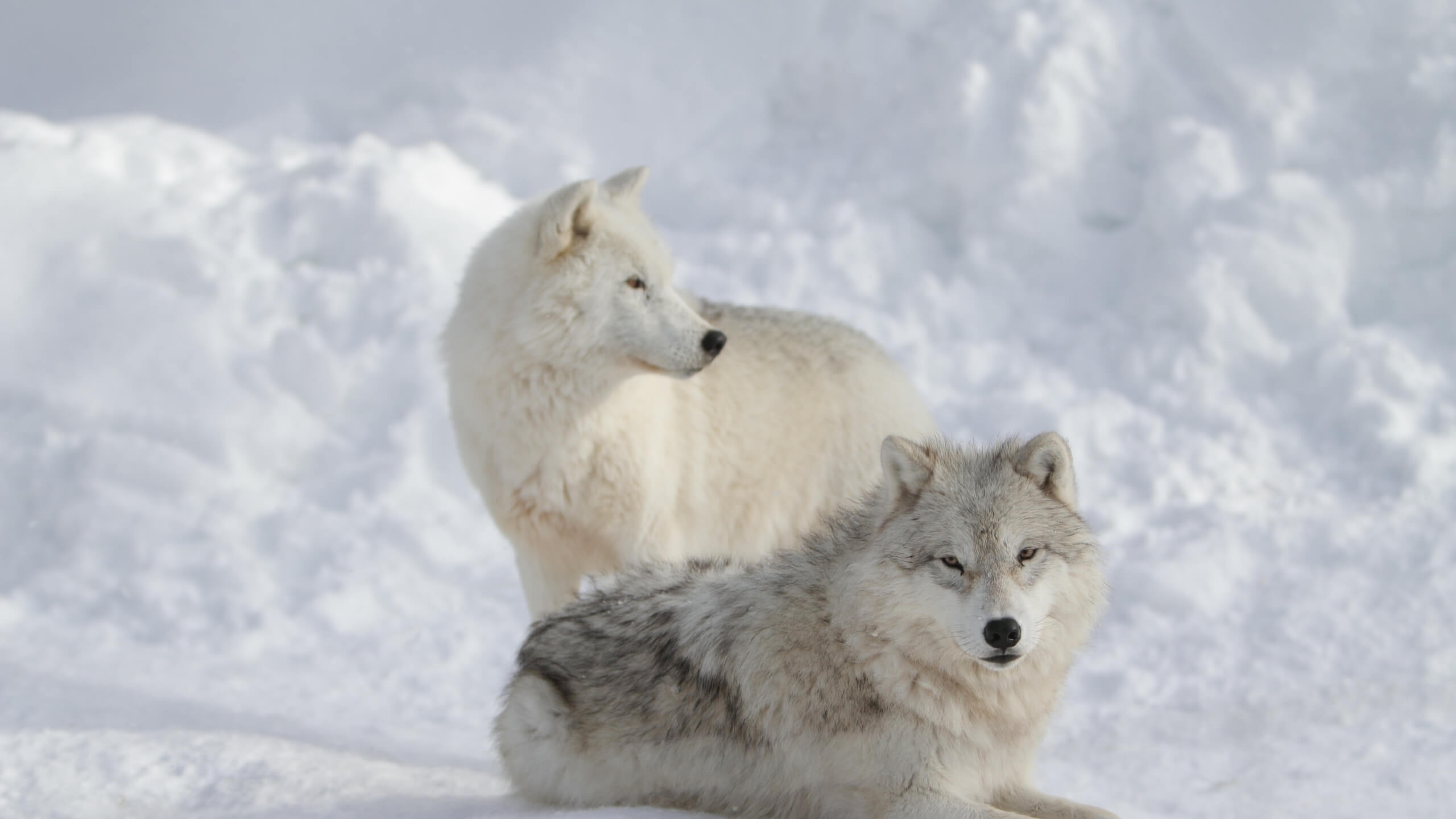
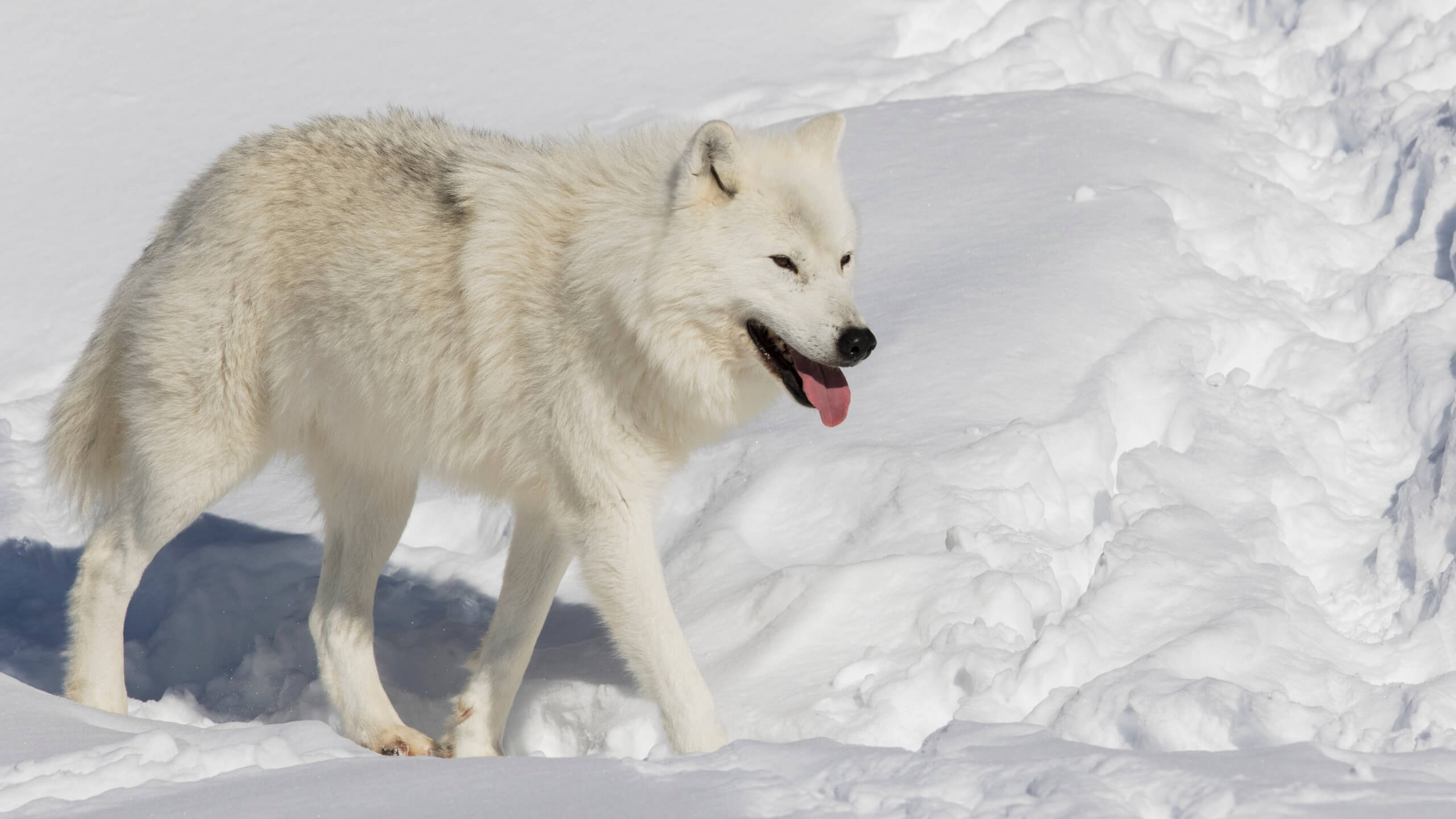
The Arctic wolf, also known as polar wolf or white wolf, is a subspecies of gray wolf. It is indigenous to the Arctic tundra regions of North America and Greenland. Arctic wolves are the apex predators in their habitat and exist at the top of the food chain.
They serve as a keystone species; keep the population of their prey species in check and have a great role to maintain balance in their ecosystem. Here we gathered information about why Arctic wolves are important and what is their role in the ecosystem.
Why Are Arctic Wolves Important?
Arctic wolves are an important part of the Arctic ecosystem. They are a keystone species in their environment and keep the population of other animals in check, such as lemmings, voles, hares, muskoxen, caribou, etc. Their prey species are mostly herbivores that eat vegetation. They regulate the population of their prey species, prevent overgrazing and keep the ecosystem healthy.
Also Read: Why are Orcas Important?
Arctic wolves eat their prey with bones and organs and help to distribute and recycle nutrients. They are also opportunistic feeders and scavenge carcasses that would otherwise take a long time to decompose in the cold tundra climate, so keep their environment clean. They also play a vital role in maintaining biodiversity within their ecosystem by providing habitat to many organisms that directly or indirectly depend on them.
Additionally, Arctic wolves compete for food sources with other predators in the region like polar bears, and so help to keep the population of other predators in control. Moreover, arctic wolves provide a deep insight into how wildlife adapt themself to climate change and other environmental issues because of their unique habitat requirements.
What Is The Role Of Arctic Wolves In The Ecosystem?
Arctic wolves are the apex predators in their ecosystem. The following are some of the main roles arctic wolves play in their ecosystem:
Ecosystem Balance
Arctic wolves are the apex predators in their ecosystem, which means they exist at the top of the food chain in their habitat. In this way, they help to regulate the population of their prey species.
Arctic wolves mostly prey on herbivores, such as muskoxen, caribou, Arctic hares, lemmings, etc. So they indirectly prevent overgrazing and contribute to maintaining their ecosystem healthy by keeping the population of their prey species in check.
Nutrient Cycling by Arctic Wolves
When Arctic wolves hunt and feed on their prey, they not only eat meat but also bones and organs and the nutrients it contains. They are also known to cache and bury surplus food for later consumption. In doing so, they contribute to the redistribution of nutrients within their territories. Their buried food serves as a nutrient source for other organisms, such as scavengers, insects, and decomposers.
Indicators of Ecosystem Health
The existence and behavior of Arctic wolves serve as an indicator of the health of the Arctic ecosystem. Their population dynamics, like their reproduction rate and survival rate, can provide insight into the overall ecological balance in the Arctic region.
Monitoring the health and thriving of Arctic wolf populations can help scientists to evaluate the impacts of global warming and climate change on the Arctic ecosystem.
Cultural and Symbolic Value
Arctic wolves have great cultural importance for native communities living in the Arctic region. They are symbols of strength, adaptability, and resilience for these people. For many native communities, the survival and flourishing of Arctic wolves have a relationship to their cultural identity and traditional lifestyle.
Conservation and Research
Research on the Arctic wolves provides information about predator-prey dynamics, interactions in the Arctic ecosystem, and adaptation to extreme environmental conditions. Scientists can get deep insights into a wide range of ecological processes by understanding the Arctic wolves’ behavior, habitat needs, and population trends.