NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) is a renowned US government agency primarily focused on aerospace and aeronautics research, and space exploration. Despite having the main mission of space exploration and aeronautics, it also collaborates with other agencies and organisations on projects involving oceanography and Earth science. After reading this article, you will know why NASA stopped exploring the ocean, what is the role of NASA in oceanography, and did NASA found an ocean world.
Why Did NASA Stop Exploring The Ocean

NASA primarily focuses on space exploration, however, it still contributes to Earth sciences including oceanography, and collaborates with agencies like NOAA. There are several reasons why NASA does not primarily explore the ocean:
Mission Focus
The primary mission of NASA is to explore space, understand Earth’s atmosphere, and do research on other planets and celestial bodies. Since its beginning, NASA has been at the front line of exploring space. It has sent Apollo missions to the Moon, rover missions to Mars, and satellite launches to study other planets and concepts in the Universe. Earth sciences, including the study of the ocean, is a part of NASA’s mission, but it is not the main focus of the agency.
Some people think that the main purpose behind the creation of NASA was to explore oceans on Earth, but soon after it started doing so, it transferred its focus to exploring outer space. But it is not true. NASA was created in 1958 to compete with the Soviet Union in the space race after its launch of the Sputnik 1 satellite.
Specialisation
Ocean exploration requires specialized equipment, resources, knowledge, and skills that NASA doesn’t have. Agencies like NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) and organizations like WHOI (Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution) are more dedicated to exploring and studying the oceans. They have expatriates and resources for it.
Budget And Resources
NASA operates its missions within a limited budget allocated by the U.S. government. Limited resources, budget, and workforce do not allow it to study Earth’s oceans on a primary basis. While NASA does conduct some Earth Science research, including oceanography, it primarily directs its resources toward space missions and related scientific efforts.
Prioritization Of Space Exploration Goals
NASA has big ambitions like sending humans to Mars, studying faraway galaxies, and developing technologies for space exploration. So the agency put most of its efforts, resources, and time into these projects. Space exploration goals are prioritized over other things like ocean exploration.
Collaboration With Other Agencies
NASA often collaborates with other governmental agencies like NOAA to collect data and do research on Earth sciences, including studies of the oceans. NASA usually brings its skills in using satellites and technology to help study the ocean better. The satellites collect data on ocean temperature, sea level, currents, marine ecosystem, and other parameters. Through the analysis of this data, scientists gain insights into ocean dynamics and the effect of climate change on marine ecosystems. Weather is also predicted from the satellites’ data, as the cooling and heating of oceans control the weather on the Earth.
What Is The Role Of NASA In Oceanography?
NASA has been studying our planet’s oceans from space for more than 20 years and plays a significant role in oceanography. The missions of its Earth Science Division (ESD) focus on studying the interconnected systems of our planet, including the oceans.
NASA launched the following two satellites to study oceans on the Earth:
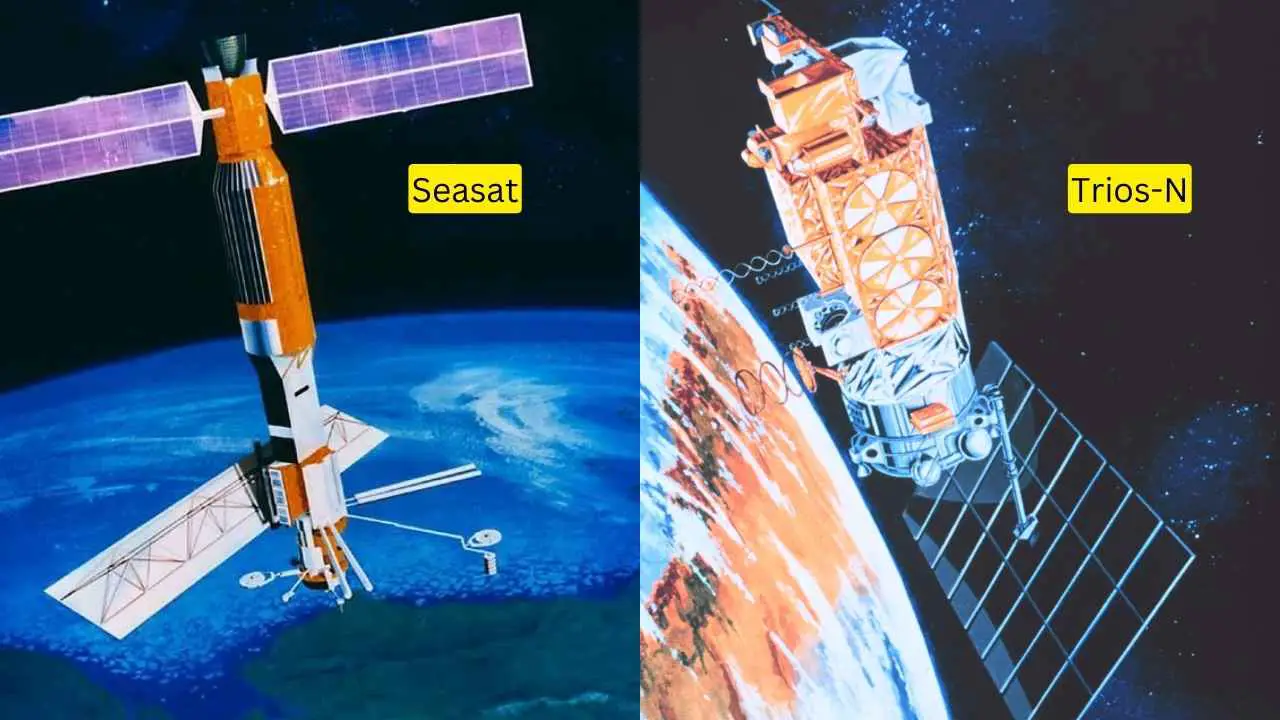
Seasat
In 1978, NASA launched its first civilian oceanographic satellite named Seasat. It was equipped with five complementary sensors designed to monitor Earth’s ocean from space. Sensors on Seasat were capable of measuring:
- The height of spacecraft above the sea surface
- The direction and speed of winds
- The temperature of sea surface
In addition, it could also identify the land, water, and cloud features, and monitor the conditions of polar sea ice.
Unfortunately, a massive short circuit stopped the work of Seasat after only 105 days. All its data-taking operations ended, but it still provided as much oceanographic data as had been provided by ships and other sources in the previous 100 years. The data and variables that Seasat provided are some of the most important knowledge of the ocean and its impact on climate.
Trios-N
In 1978, NASA launched another satellite, named Trios-N. It was equipped with an AVHRR (Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer) sensor, which provided maps of sea-surface temperature. It also had Coastal Zone Color Scanner, which provided the first-ever maps of chlorophyll and primary productivity in our planet’s ocean.
Nowadays, there are several ocean-observing satellite missions and a large-scale scientific research community studying these data and contributing to the knowledge about the ocean. Scientists can now investigate the effect of oceans on the development of weather, hurricanes, and climate by using remote sensing data and computer models. Weather is also predicted in this way, as the cooling and heating of oceans control the weather on the Earth. It also humidifies and dries air as well as controls the speed and direction of the winds.
Did Nasa Find An Ocean World?
Ocean worlds means places (planets, dwarf planets, or moons) beyond our Earth with a considerable amount of liquid water. As liquid water is one of the three main ingredients life needs to survive besides organic molecules and energy.
Astrobiology is the search and study of life in the universe beyond our Earth. We are learning that ocean worlds could be found or ever-present in the galaxy. In our Solar System, NASA found evidence of oceans on the Titan and Enceladus moons of Saturn, the Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto moons of Jupiter, the Triton moon of Neptune, and on the dwarf planet Pluto. Scientists also believe that our Earth’s neighbor planets Venus and Mars may have had oceans billions of years ago.
NASA contributes to research on our Earth’s oceans and helps to provide better knowledge about the role of oceans in the climate system of Earth. A better knowledge about Earth’s oceans will help to better understand worlds beyond our planet Earth.