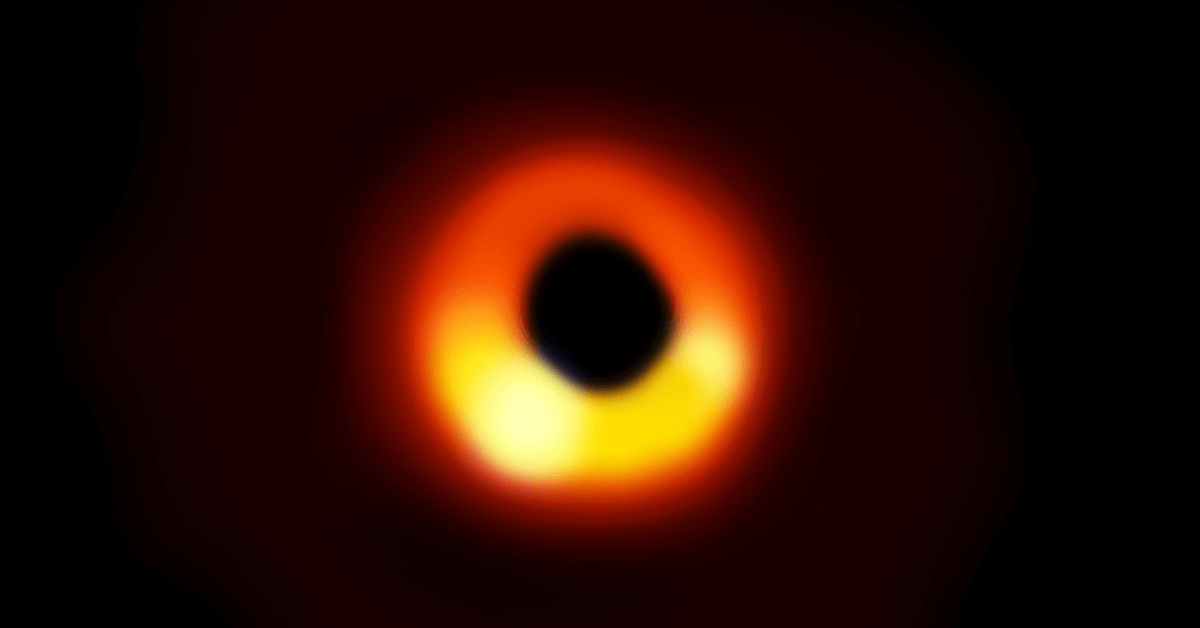
What exactly is a Black Hole?
- An incredibly dense sphere with immense gravity where nothing (mass or light) can escape out is known as a Black Hole.
- Black holes are invisible and not black, since, they just don’t escape light doesn’t mean they are black in colour.
- According to an observer, time appears to freeze in black holes, mainly it slows down due to high gravity pressure.
- They are thought to be very deep and things happen to fall directly into the singularity.
- “Albert Einstein” first noticed but was also in denial of black holes (1916). Eventually, the first black hole existence got discovered in the year 1971.
- The three types of black holes are identified based on their size: Stellar, intermediate, and Supermassive Black holes.
- A black hole keeps eating dust, gases and crushed pieces of dead stars from the surroundings in order to grow bigger and bigger.
Types of Black Holes:
- Stellar Black Holes are the smallest of all types of black holes. Primarily they are dead stars inside. The large star that collapses by burning through the last drop of its fuel will compress itself and create a stellar black hole.
- Intermediate Black Holes falls in the category of medium-sized black holes and are comparatively difficult to find in space.
- Supermassive Black Holes are categorized as the biggest of all types of black holes. They contain the mass of more than millions or billions of the Sun. Scientists believe Earth itself continuously orbits a supermassive black hole right in the centre of the Milky Way.
- The procedure to grow bigger for every type of black hole is the same. They keep growing by eating up dust particles, ashes of dead stars and absorbing gases.
What is a black hole made of?
- The procedure begins from the point where huge stars lose the very last drop of their fuel, become dead, and come under their own weight. Due to this weight, they get collapsed. All the matter gets collected in “singularity” and that’s how black holes come into being. Hence, black holes are thought to be made of huge masses of dead stars.
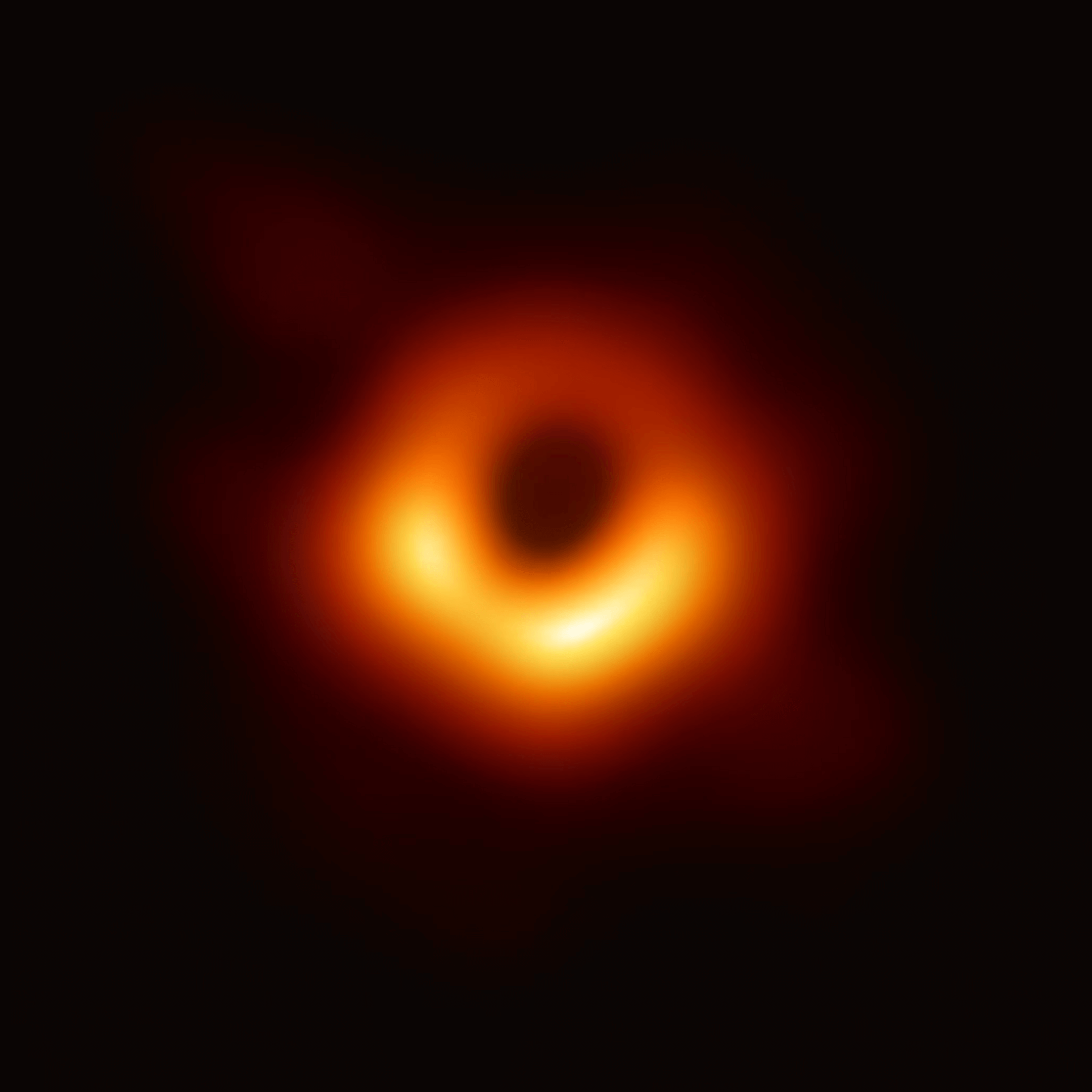

Is there matter in a black hole?
- Yes, the matter exists in black holes, all the matter gets collected in the centre of it. This centre of a black hole is known as “Singularity” (A place where all the matter falling into the black holes is crushed, squeezed, composed and finally placed in).
Does time stop in Black Hole?
- The time in black holes is mainly influenced by its high gravity pressure due to which it becomes so slow that it feels frozen to an observer outside, in certainty, it does not stop.
Do black holes kill you if you fall into them?
- Yes, they will tear you apart because gravity pressure inside a black hole is so strong. Some astronomers believe that small black holes (stellar black holes) won’t be that harsh on you. But always keep in mind that anything going into a black hole or just cruising around its horizon will never bounce back.
What happens if you go inside a black hole?
- Stepping into a black hole can make you spaghetti. Sounds weird! but it’s true because the moment you enter a black hole, immense gravity over there will immediately direct you in such a manner that you will look like spaghetti. And this is one of the most horrifying things about black holes, once you have stepped into it, you can never escape out.
Density of a black hole?
- It is considered that the density of the black holes is approximately 4 x 1014 g/cm3.
Do time and space exist in a black hole?
- Time inside the black hole appears to be frozen to an observer. In reality, time just slows down due to the immense pressure of gravity.
- About space, astronomers believe that a black hole is a limited place, starting from the edge of the black hole it ends at its singularity, whereas, outside, its (black hole) space is absolutely infinite.
What happens to the Star near the Black Hole?
- The stars or any other sort of mass around the horizon of black holes behave differently than other masses in space due to the immense gravity in black holes which keeps attracting them to themselves in order to crush them into small pieces and collect them into the singularity.
Does a Black Hole decay?
- Yes, black holes eventually decay because energy particles keep evaporating by making their way through the event horizon, leaving it shrunk or collapsed. The event appears due to the realistic quantum effect.
- The entire concept was explained by Stephen Hawking in Theory Hawking Radiation (1974).
Is it possible to survive a black hole?
- There are two concepts behind the survival of humans visiting black holes.
- Some astronomers believe that humans can survive through Stellar black holes because the stretching force over there is less as compared to supermassive black holes, whereas, a supermassive black hole will stretch you in such a manner that you will look as plain as spaghetti and will fall into singularity.
Facts about Black Hole:
- Black holes are invisible because they do not allow light to escape.
- Black holes can rip apart the stars which are closer to them.
- The time of a black hole is quite slow if compared to Earth due to the high gravity pressure.
- According to a recent study, the nearest black hole is expected to be between 1000 to 1500 light-years away.
- Matter exists in black holes. All the matter is squeezed into one single place called “singularity”.
- A black hole is a one-dimensional place because none can bounce back.