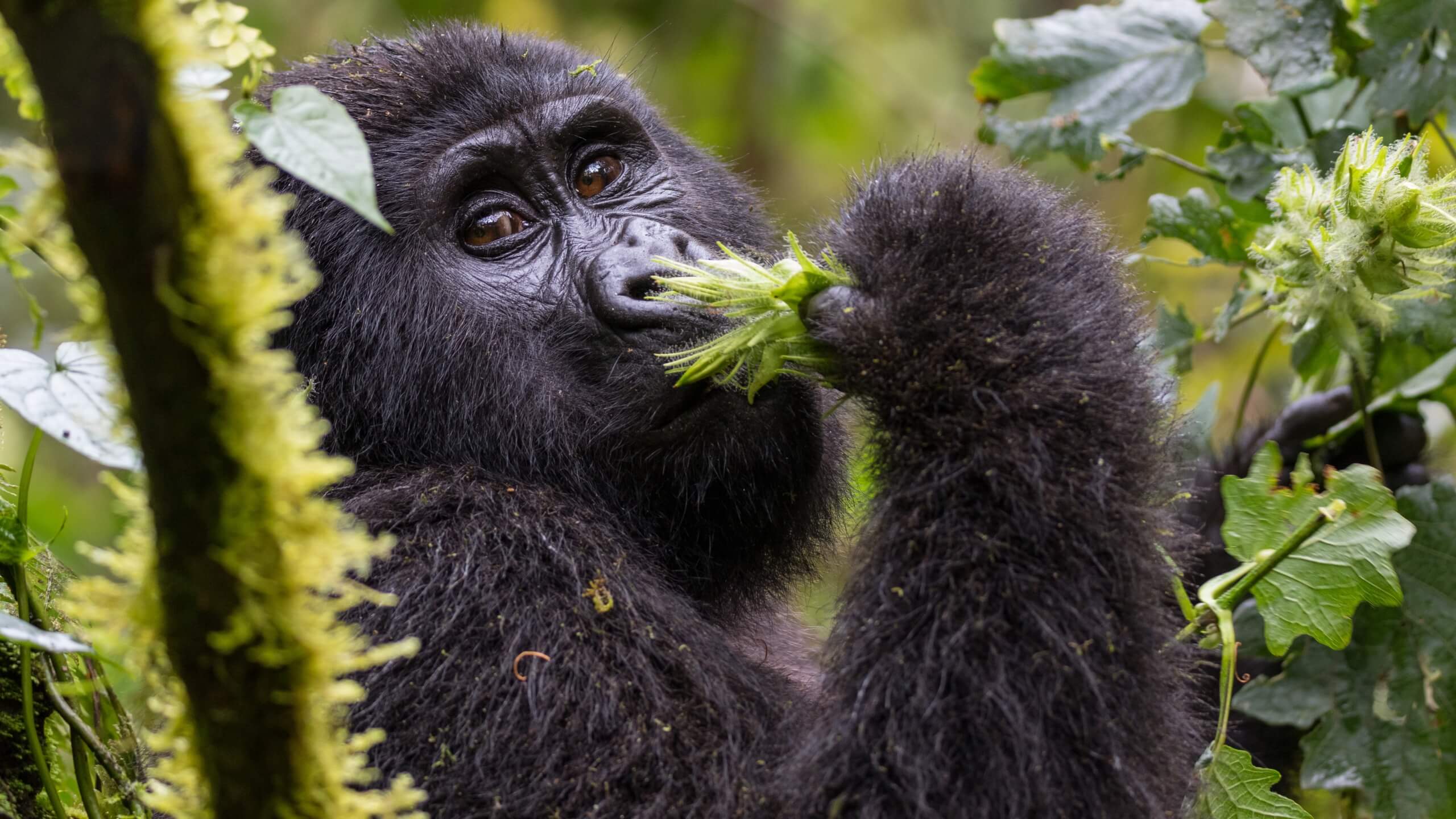
Gorillas are the majestic creatures of the African tropical forests. They are extremely important because they are the keystone species of their habitat and have a great effect on their natural environment. Gorillas also act as an umbrella species for their ecosystem and help to preserve biodiversity on a large scale. Here we gathered all information about why gorillas are important and what would happen if they become extinct.
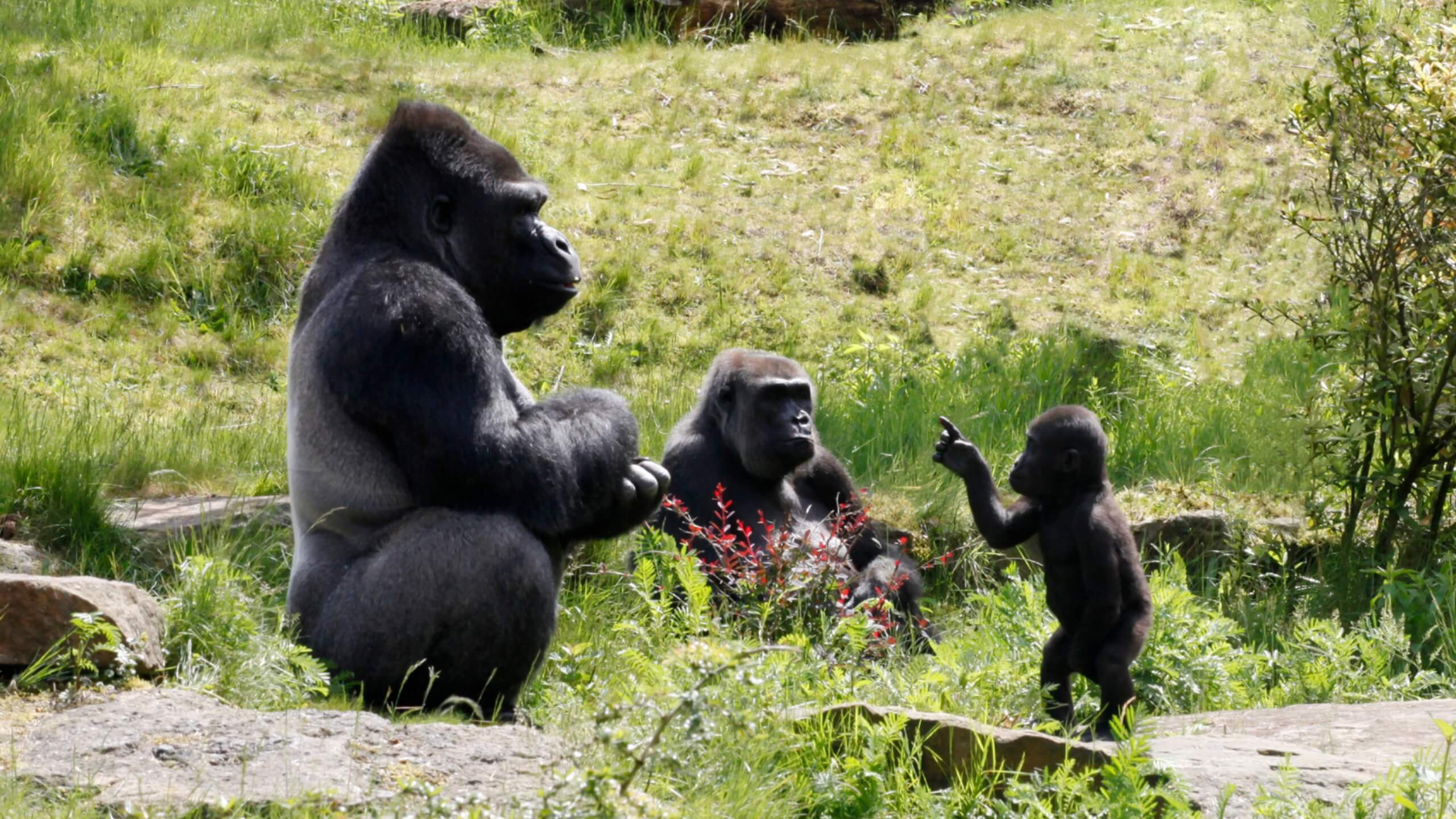

Why are Gorillas Important
Gorillas are important for many reasons, including their ecological, cultural, and scientific significance. Here are some of the key reasons why gorillas are important:
Ecological importance:
Gorillas play a critical role in maintaining the structure and function of their ecosystem. They are a keystone species, which means that their impact on the ecosystem is greater than their actual population size. Gorillas are herbivores and they consume large amounts of vegetation every day. This helps to control vegetation growth, which in turn affects the availability of resources for other animals in the ecosystem. Gorillas also serve as an important food source for predators such as leopards, which helps to regulate predator-prey dynamics in their ecosystem.

Cultural significance:
Gorillas are an important cultural icon in many parts of Africa, and they have played a significant role in the culture and traditions of local communities. They are often seen as symbols of strength, intelligence, and protection, and they are revered in many African cultures.
Scientific importance:
Gorillas are one of our closest living relatives, and studying their behavior and biology can provide insights into our own evolution and behavior. Gorillas are also important for medical research, as they are susceptible to many of the same diseases as humans, including Ebola and COVID-19.
Biodiversity:
Gorillas are part of the rich biodiversity of our planet, and their conservation helps to maintain the health and diversity of their ecosystem. Protecting gorillas also helps to preserve the many other species that share their habitat, including other primates, birds, and mammals.
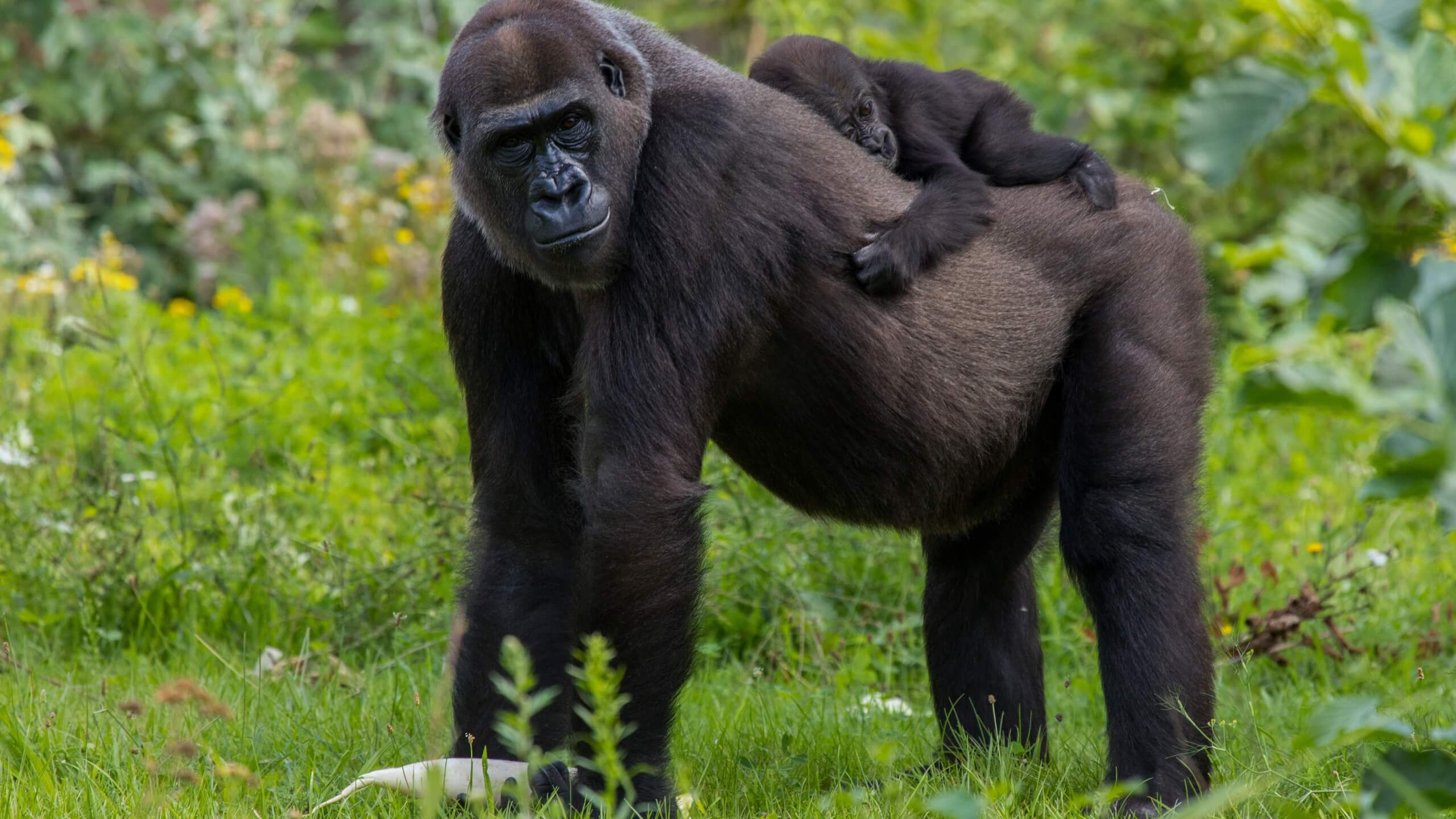

What would happen if gorillas went extinct?
If gorillas were to go extinct, it would have significant impacts on their ecosystem and the surrounding environment. Gorillas play a vital role in their habitat, and their loss would have ripple effects throughout the ecosystem. Here are some of the potential impacts of gorilla extinction:
Disruption of food webs:
Gorillas are herbivores, and their feeding habits have a significant impact on the vegetation in their habitat. If gorillas were to go extinct, there would be an increase in the amount of vegetation, which could lead to a reduction in the availability of resources for other herbivores. This could result in a decline in herbivore populations and a subsequent decline in predator populations.
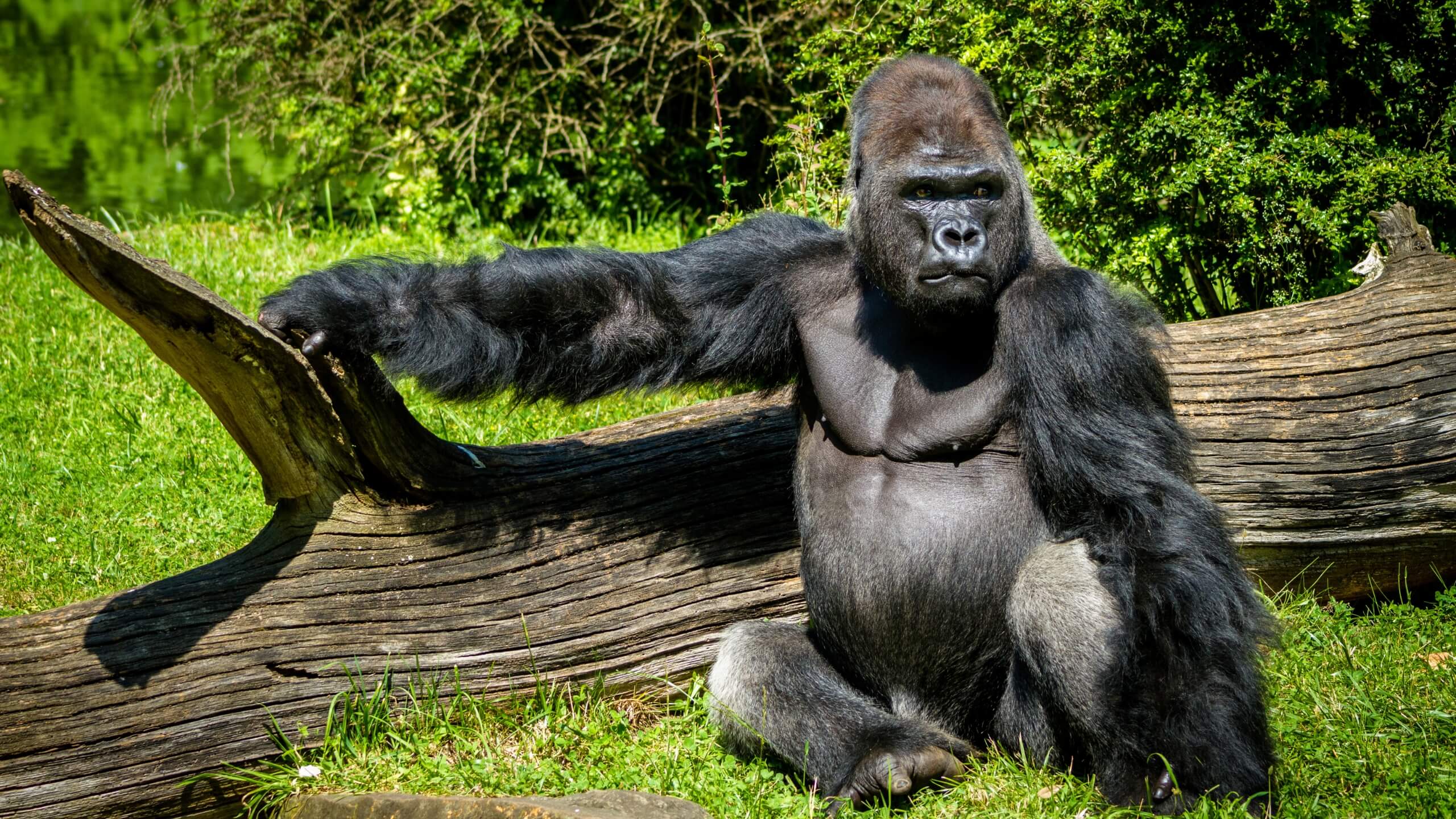

Loss of seed dispersal:
Gorillas are important seed dispersers, as they eat large amounts of fruit and then excrete the undigested seeds throughout their habitat. This helps to promote the growth of vegetation and maintain biodiversity in the ecosystem. If gorillas were to go extinct, there would be a significant reduction in seed dispersal, which could lead to a decline in the health and diversity of the ecosystem.
Carbon sequestration:
Gorillas play an important role in carbon sequestration, which is the process by which carbon is removed from the atmosphere and stored in the soil or vegetation. By promoting the growth of vegetation through their feeding habits, gorillas help to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. If gorillas were to go extinct, there would be a reduction in carbon sequestration, which could contribute to climate change.

Loss of ecotourism revenue:
Gorillas are a major attraction for ecotourism in some parts of Africa, and their loss could have economic impacts on local communities. Ecotourism revenue can provide incentives for conservation efforts, and without gorillas, there would be a reduction in the number of tourists and associated revenue.
Loss of cultural significance:
Gorillas have played an important role in many cultures throughout history, and their extinction could lead to a loss of cultural heritage and traditions.
Why are gorillas keystone species?
Gorillas are considered a keystone species in their ecosystem, and that their impact on the ecosystem is greater than their actual population size. To understand this in more detail, let’s first define what a keystone species is.
A keystone species is a species that plays a critical role in maintaining the structure and function of an ecosystem. If a keystone species is removed from an ecosystem, the entire ecosystem can be disrupted or even collapse. This is because keystone species have a disproportionate impact on their ecosystem, despite their often small population sizes.
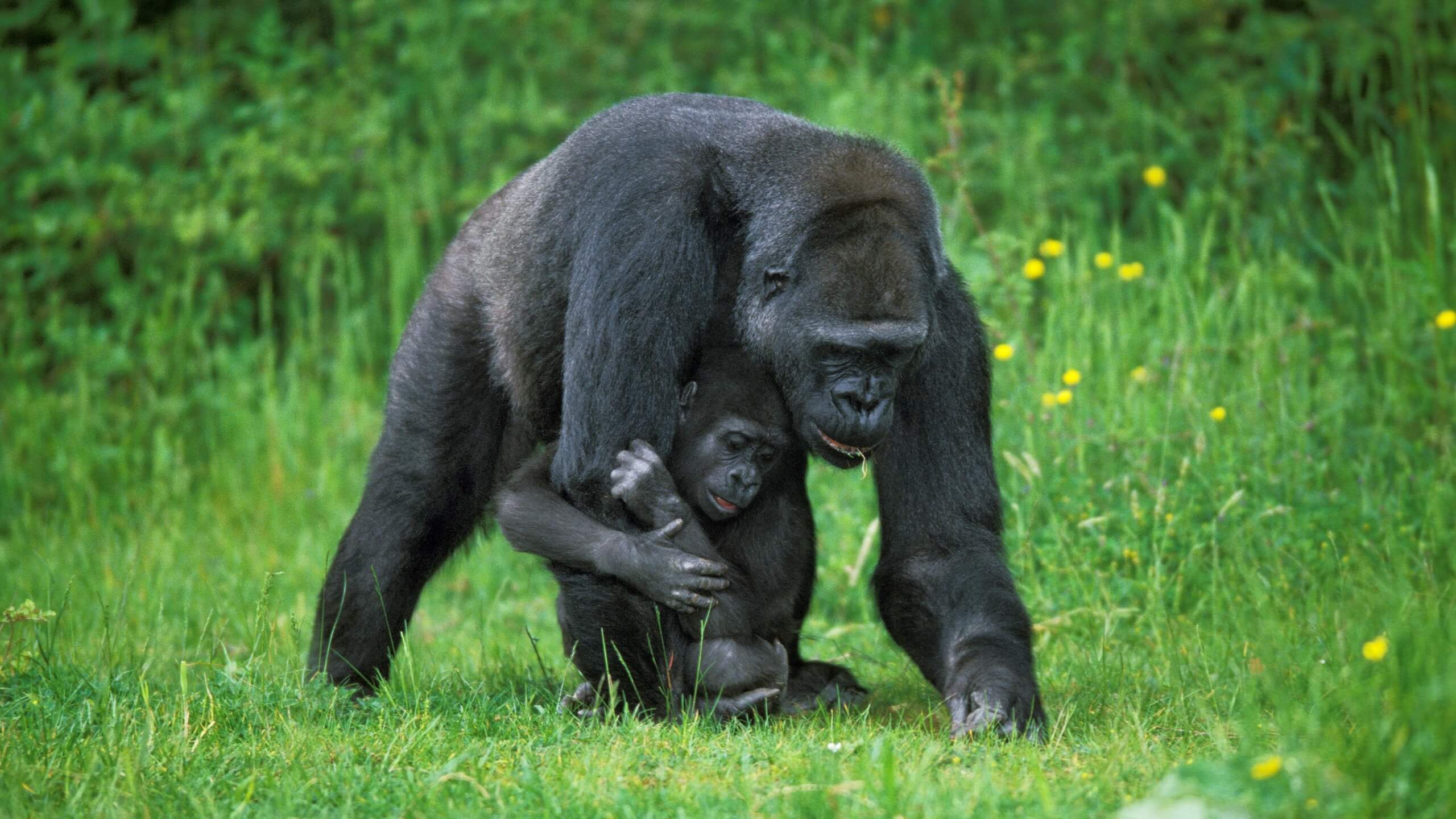

Gorillas are considered a keystone species because they have a significant impact on the vegetation in their habitat. Gorillas are herbivores and they consume large amounts of vegetation every day. This consumption helps to control vegetation growth, which in turn affects the availability of resources for other animals in the ecosystem. For example, if gorillas were to become extinct, there would be a significant increase in the amount of vegetation, which could negatively impact the availability of resources for other herbivores in the ecosystem.
Furthermore, gorillas are also an important food source for predators such as leopards, which helps to regulate predator-prey dynamics in their ecosystem. By controlling the population sizes of herbivores and providing food for predators, gorillas help to maintain the balance of the ecosystem.
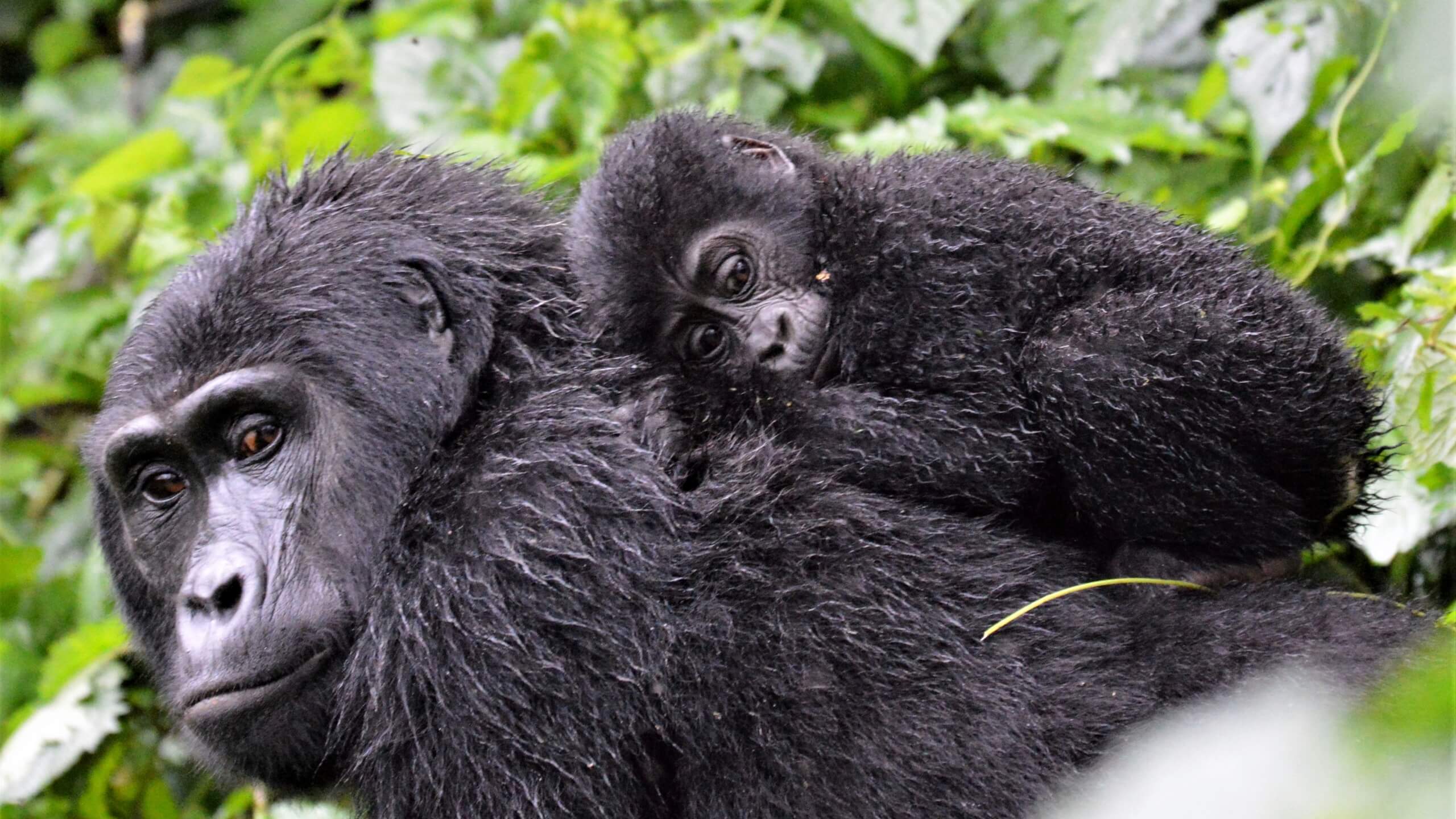

Why are gorillas important to humans?
Gorillas are important to humans for many reasons, such as:
- Gorillas share up to 98% DNA with humans and are one of our closest relative animal species. They provide us with valuable insight into our evolutionary history.
- Gorillas are essential for the maintenance of biodiversity and a healthy ecosystem in their native habitat. They disperse seeds and help many plant species to preserve and thrive. They also provide shelter and food sources for other animals in their ecosystem.
- Gorillas also help scientists to better understand the impacts of climate change on wildlife populations throughout the world.
- Additionally, gorillas attract ecotourists and play an important role in boosting the local economy.