The estimated cost of the James Webb was just $4.96 billion (2014) but it ended up being a megaproject and eventually cost about 10 billion USD. But “Why Is James Webb So Expensive?”
NASA reconstructed the entire project due to which the construction cost was already raised to 8.8 billion USD by 2018, whereas the actual construction of Webb was initiated in 2004. From 2018, the deployment was further delayed due to some serious technical issues for at least 3 years till 2021. This delay added another billion dollars to the total cost of the Telescope.
Also read: How does the James Webb telescope work?
Some technical reasons for James Webb Space Telescope which makes it so expensive in comparison with Hubble Space are explained below:
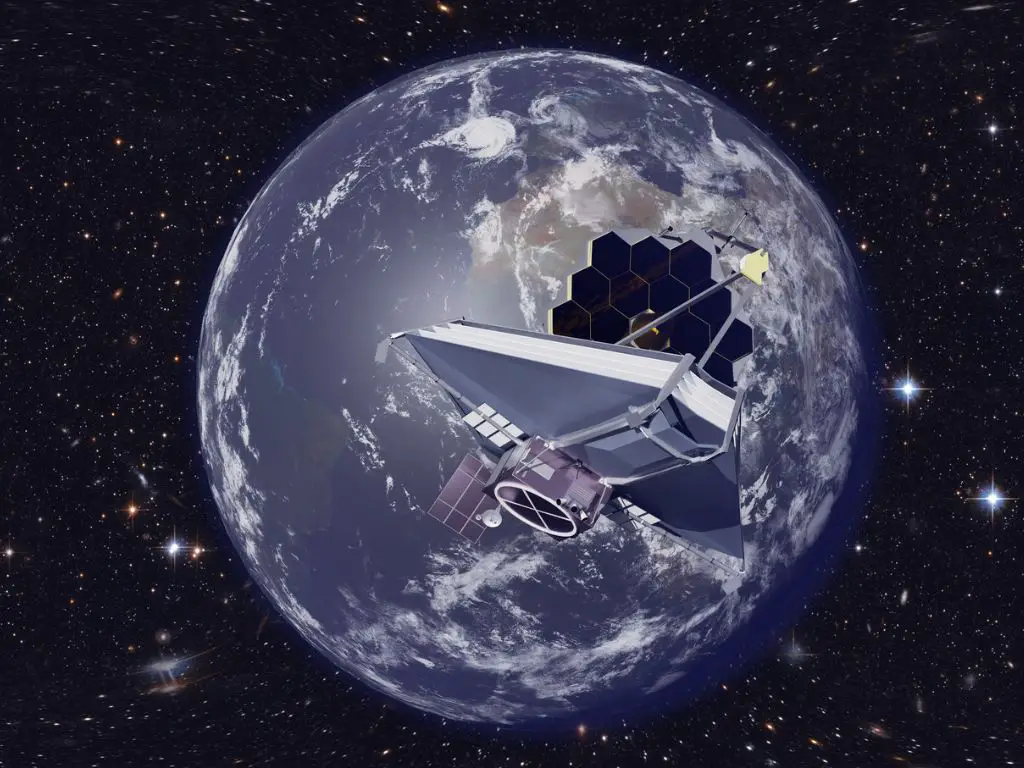
- Hubble is just above the surface of Earth, about 340 miles, however, JWST is destined to rest at Lagrange point 2 or L2 (a point of gravitational balance, away from the Sun on the far side of Earth) which is about 1 million miles above the Earth in order to keep the telescope cold enough for its infrared detectors to work properly.
- Which in the case of Hubble space was totally opposite. HST is unable to stabilise its dazzling infrared detectors due to the immense heat it absorbs from the Sun and the Earth as well.
- JWST has a deployable sunshield (the size of a tennis court) made of five layers of an aluminium-coated space blanket material called Kapton. These five layers of ultralight Kapton are efficiently made to absorb heat.
- The spaces or gaps between the layers allow heat to be perfectly radiated away from the telescope, whereas Hubble Space is directly exposed to the Sun’s rays and it also absorbs the heat of Earth due to which its infrared detectors are dazzled and the telescope can not see distant objects.
- The Hubble Space Telescope has a mirror 7.8 feet in diameter and is limited, whereas, Jwst has a 21-foot mirror that will not just take more clear images but also, it will take less time to complete its task than Hubble could. James Webb is so big that its wide mirror has to be folded into an origami-style (the Japanese art of paper folding) to fit inside Ariana’s 5 space rockets.
- Shockingly this entire 21-foot, 18 hexagonal segmented mirror weighs just 6.5 metric tonnes as compared to Hubble space’s mirror which is relatively smaller in size but heavier. The ultralight beryllium metal caused the JWST mirror to be this much light weight as compared to the 11.1 tonnes of the Hubble Space Telescope.
Scientists had had an unexpected experience of short-sightedness (caused blurry shots taken by HST) with the Hubble Space Telescope (launched in 1990) which was then corrected by a group of astronauts, sent to fix the problem. The Hubble Space Telescope was lucky enough to receive glasses. However, in the case of JWST, any mission required to correct technical issues is nearly impossible hence no failures are allowed but scientists have informed that JWST is a prototype and in prototypes, there is always a chance of mistake (says, experts).
This is why NASA has spent almost 20-24 years building and making sure that each and every part of the telescope has no chance of mistake or problem. The entire procedure of building and testing the telescope cost NASA an immense amount of money, energy, and time.
Scientists believe that this much investment and delay will eventually be worth the outcome. JWST is the successor of Hubble Space and is built under circumstances to perform better than Hubble Space in almost all possible ways. With its ability to look deep into space and time, it will eventually provide unimaginable rewards to our scientific knowledge.