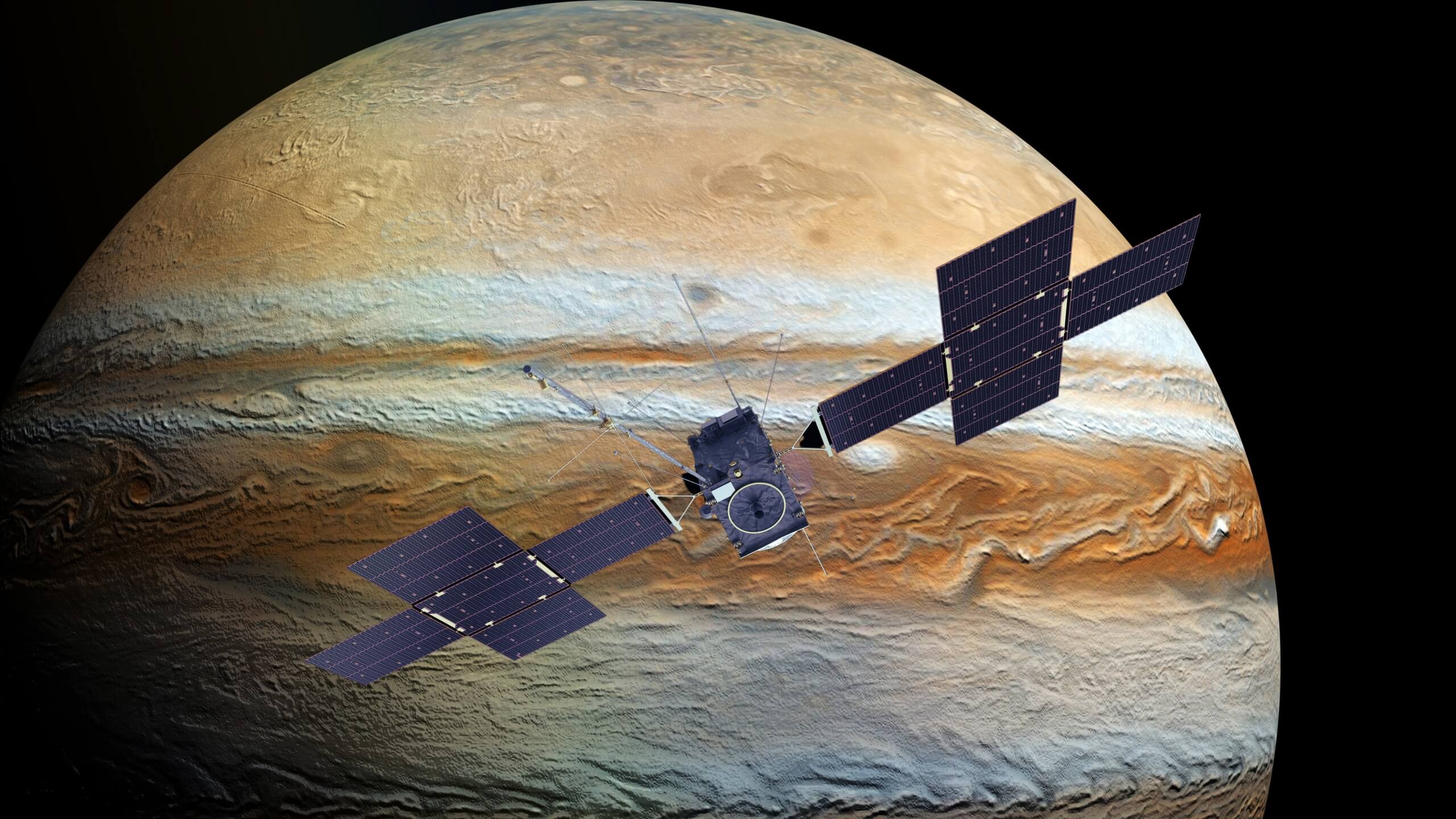
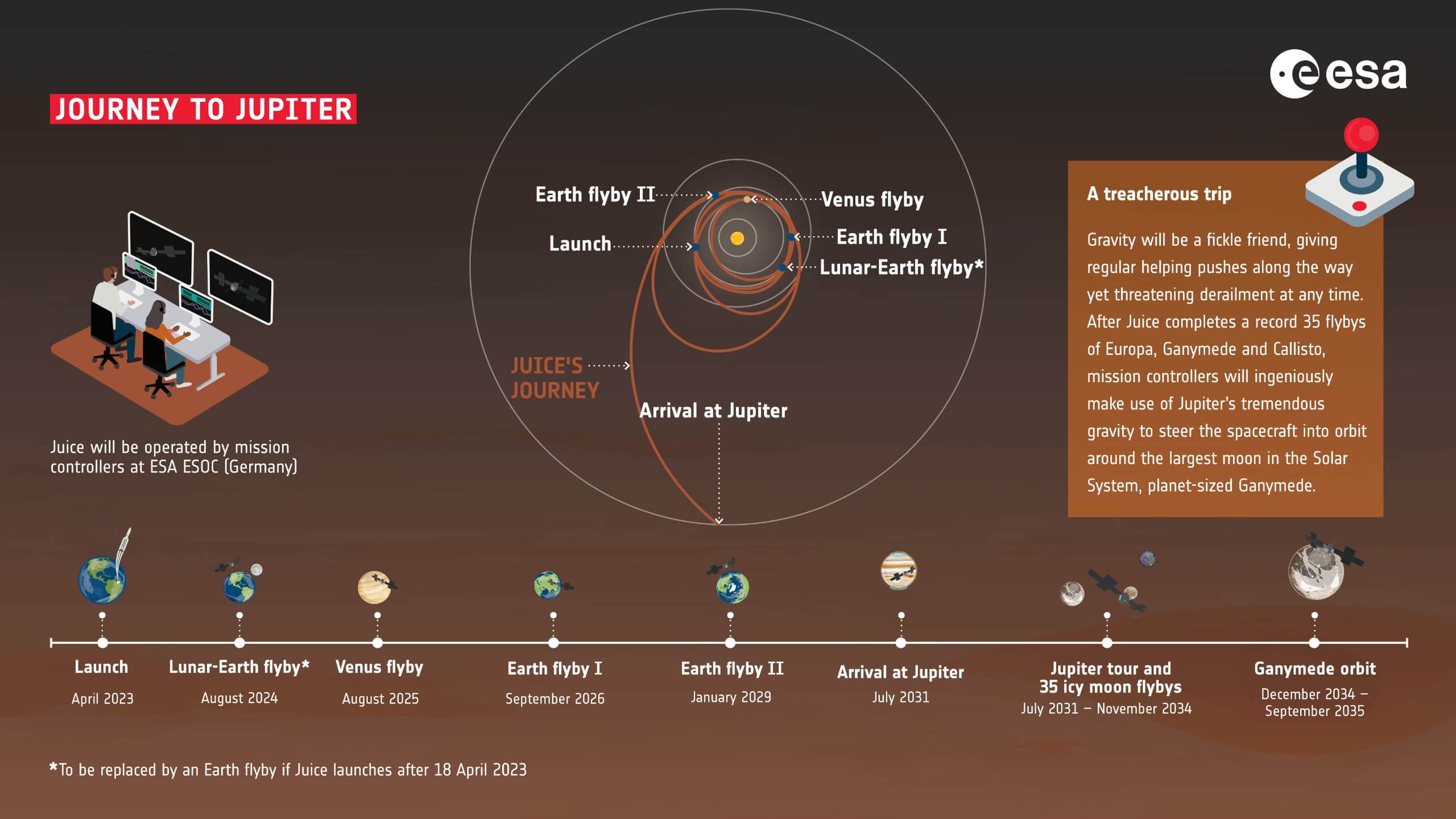
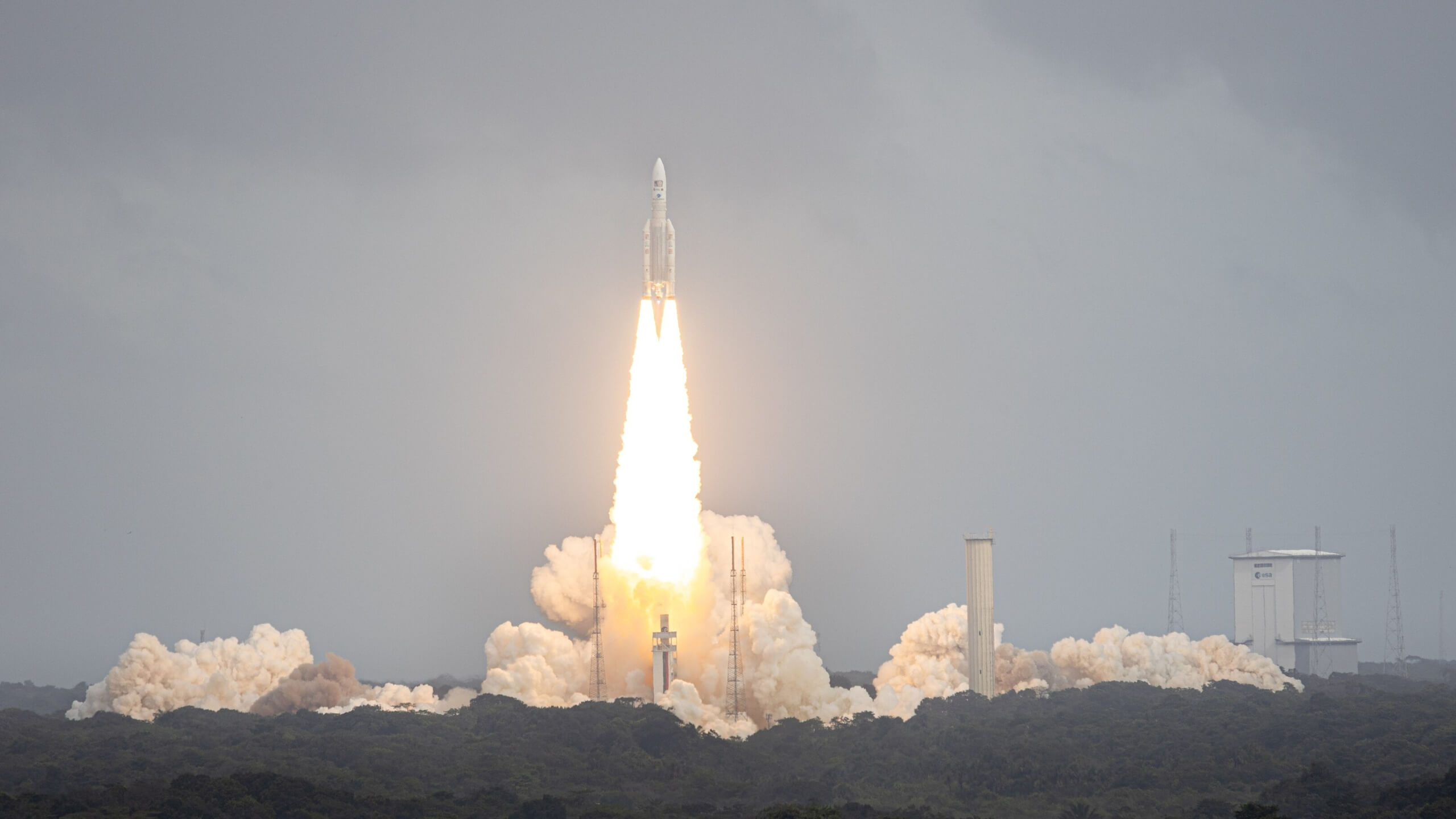
Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE)is a mission launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) to explore Jupiter and its three large icy moons named Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa. This mission aims to find these moons as planetary objects and possible habitats as well as to explore Jupiter’s complex environment. The explorer was launched on April 14, 2023, using an Ariane 5 launch vehicle in French Guiana. It will take 8 years for JUICE to reach its destination.
What are the primary objectives of the JUICE Mission?
JUICE (Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer) mission will keenly observe Jupiter and its three large ocean-bearing moons; Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa. The mission will investigate the potential for life on these icy moons and contribute to our understanding of the solar system by making multiple flybys of Jupiter.
Also Read: Is there life of Europa Moon of Jupiter?
Which celestial body will the JUICE Mission focus on?
The JUICE mission to Jupiter will mainly focus on studying Ganymede and Callisto. These moons are of particular interest because they are believed to have subsurface oceans and potentially habitable environments.
When was the JUICE Mission launched?
The JUICE mission was scheduled to launch on April 14, 2023. It will take eight years for the spacecraft to reach its destination in December 2031. The mission involves three returns to Earth and close flybys of three of its main moons: Europa, Ganymede and Callisto.

What will the JUICE Mission study on each of Jupiter’s moons?
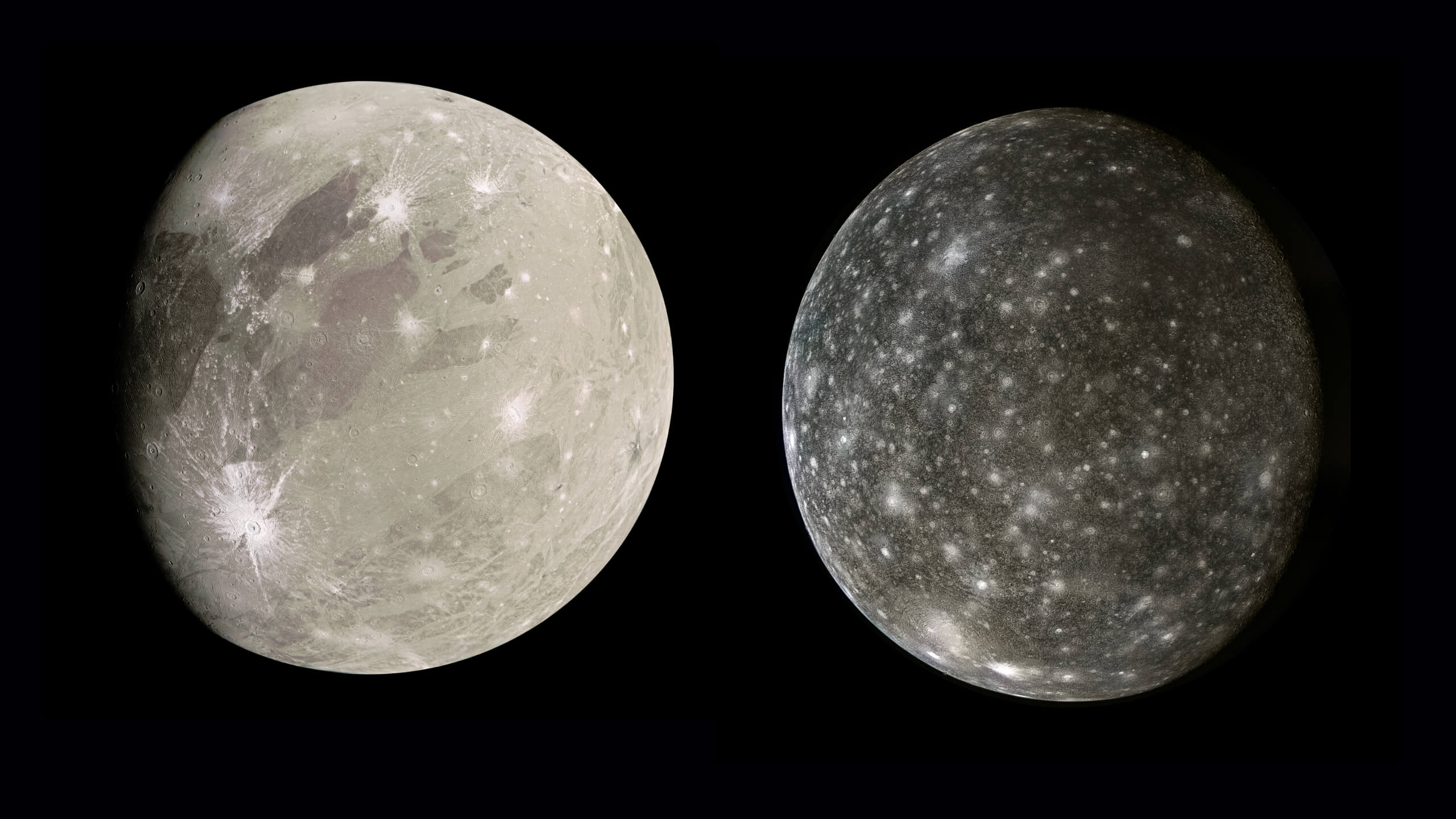
Ganymede:
Ganymede is the most focused celestial body for JUICE. It will study Ganymede’s magnetic field and its interaction with Jupiter’s magnetosphere. Moreover, it will also study the surface features of the moon, such as craters, grooves, and ridges, to better understand its geological history.
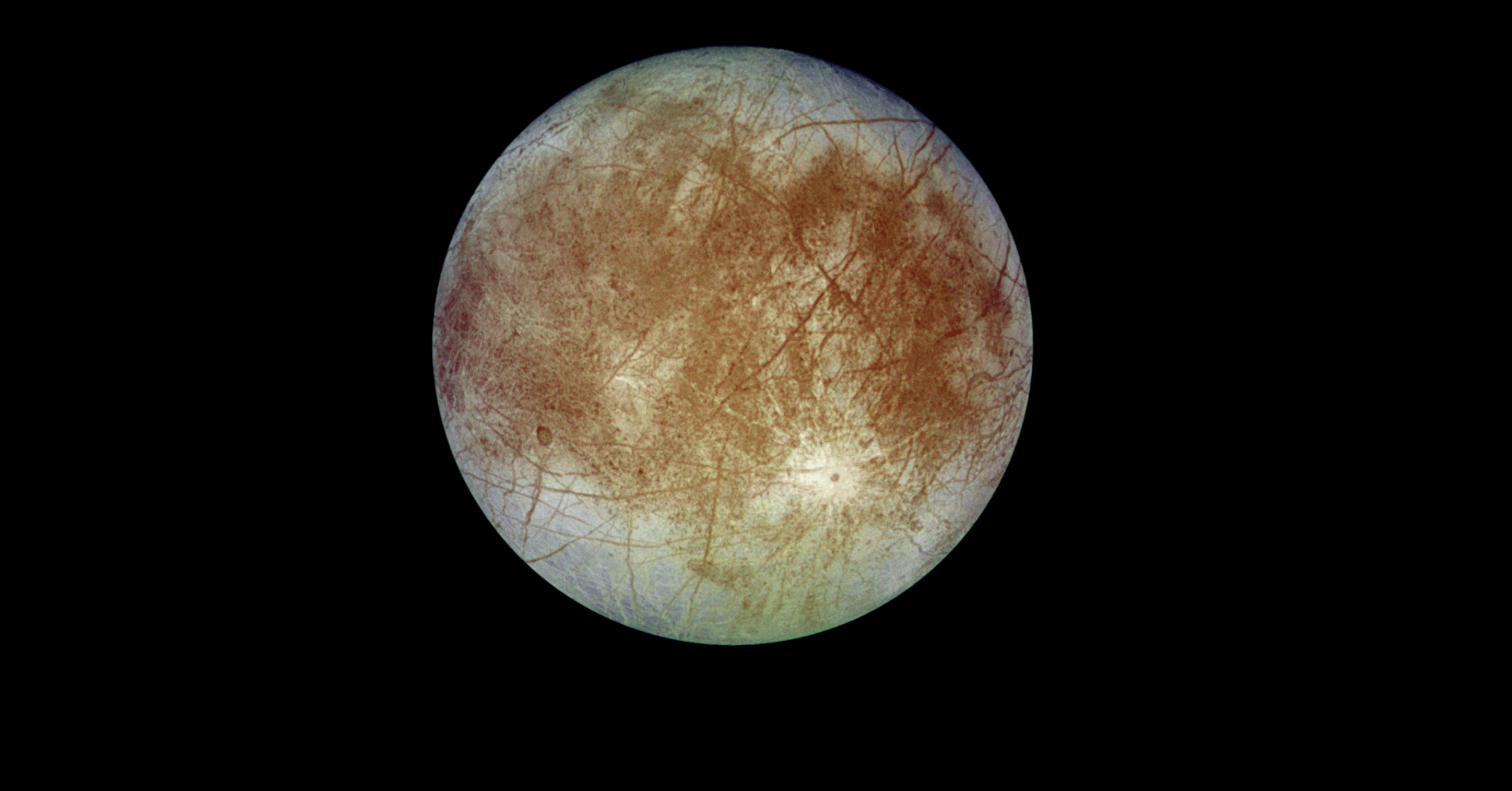
Europa:
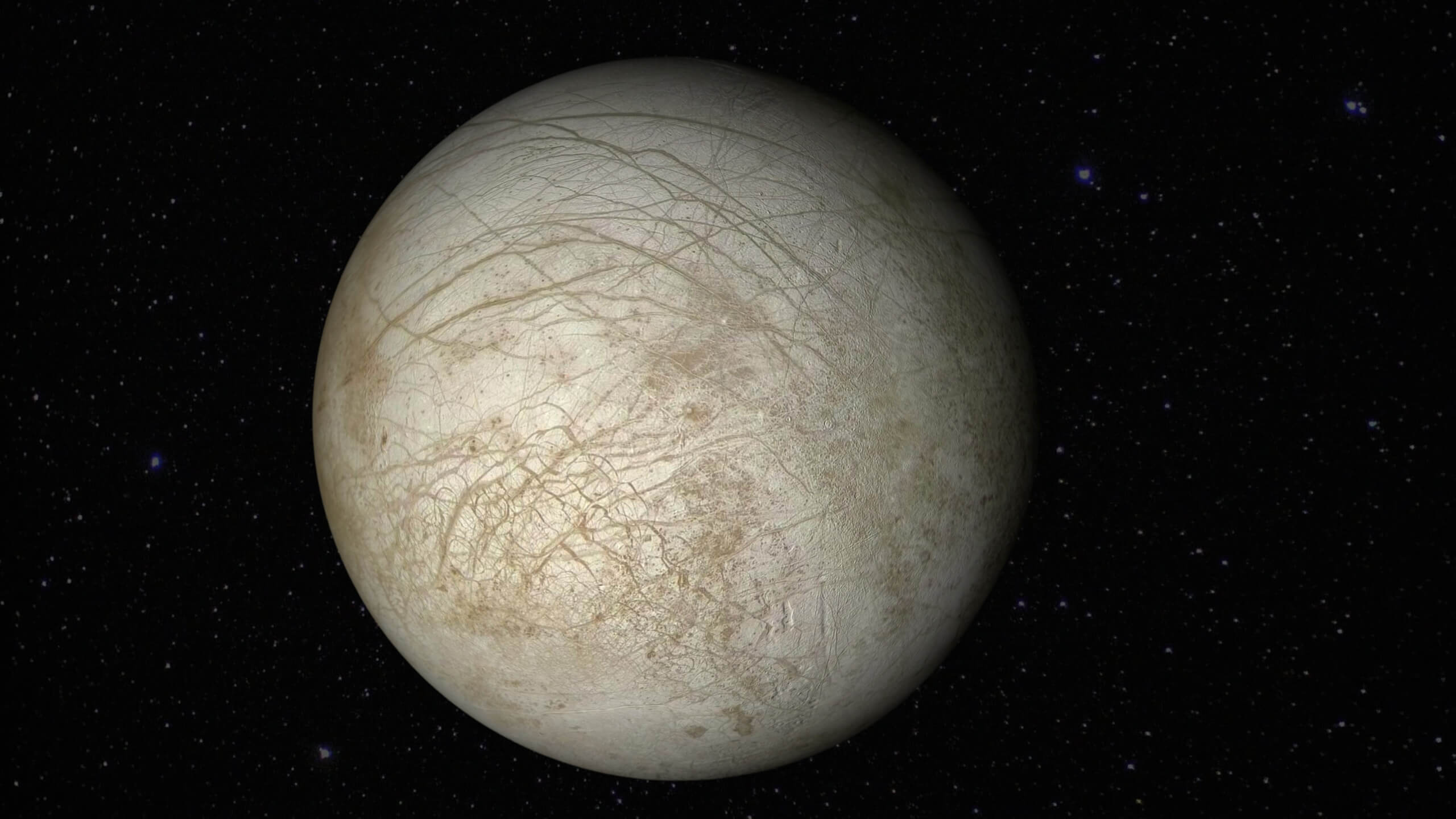
This juice space mission will study Europa’s ice shell, surface geology, and the processes that shape its terrain. The mission will also investigate for evidence of plumes erupting from its subsurface ocean.
Callisto:
The mission aims to understand Callisto’s geological evolution, magnetic field and its interactions with Jupiter’s environment.

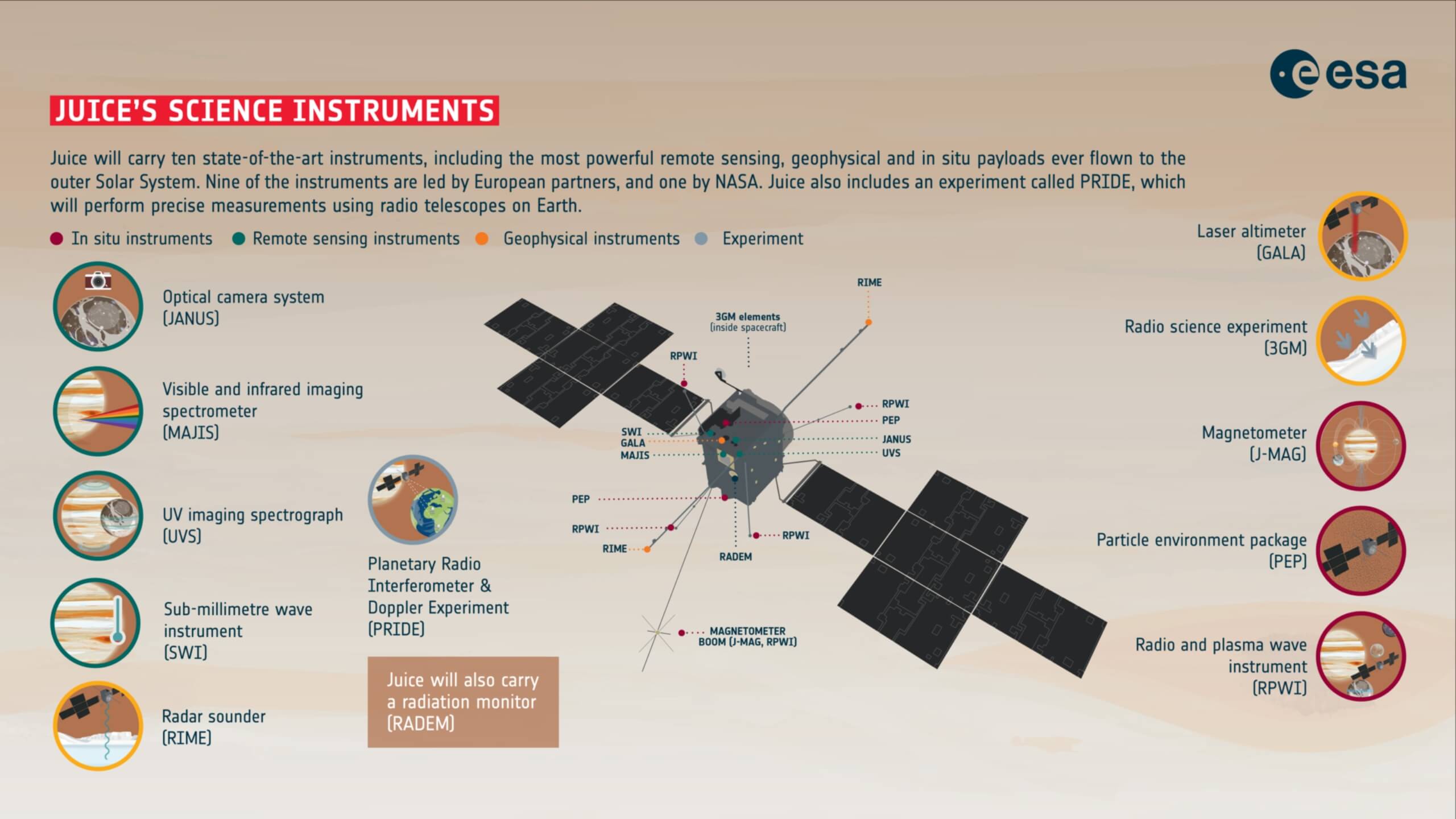
What instruments and experiments are onboard the JUICE spacecraft and how will they gather data?
Here are some of the key instruments and experiments onboard the JUICE spacecraft:
1. JUICE Particle Environment Package (PEP):
PEP consists of various sensors to study the composition, energy, and distribution of particles, providing insights into the magnetospheric interactions and plasma dynamics of Jupiter.
2. Radar for Icy Moon Exploration (RIME):
RIME is a radar instrument that will penetrate the icy crusts and map the subsurface layers to study the moon’s geological history.
3. GALA (Ganymede Laser Altimeter):
GALA is a laser altimeter specifically designed for Ganymede (the largest moon of Jupiter) which will measure the moon’s topography and surface roughness. It will provide detailed information about its geology and the presence of tectonic features.
4. MAJIS (Moons And Jupiter Imaging Spectrometer):
MAJIS is a hyperspectral imaging spectrometer that will analyze the surface materials, and identify different types of ice and minerals.
5. UVS (Ultraviolet Spectrograph):
UVS will study the ultraviolet emissions from Jupiter’s atmosphere and will determine the composition and dynamics of the gas giant’s upper atmosphere.
6. GANDALF (Ganymede Neutron Detector for Advanced Layering of Fluid):
GANDALF is a neutron detector that will measure the abundance and distribution of hydrogen and other elements in Ganymede’s subsurface.
Will the JUICE Mission search for signs of life?
Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer mission will contribute to the search for signs of life in our solar system. It will focus on three of Jupiter’s largest moons: Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto and potentially discover evidence of past or present life forms.
While the mission won’t directly search for microbial life, it will provide valuable insights and pave the way for future missions explicitly designed to search for signs of life on these intriguing moons.
How will the JUICE Mission study Jupiter’s magnetic field?
Magnetometer:
JUICE will carry a highly sensitive magnetometer instrument to measure and map Jupiter’s magnetic field which will provide detailed information about the strength, structure, and variability of the magnetic field.
Interactions with Ganymede:
JUICE will closely observe Ganymede, the largest moon in the solar system and the only one known to have its own magnetic field. This investigation will help uncover details about Ganymede’s internal structure and the processes that generate and sustain its unique magnetic field.
Radiation and Plasma Investigation:
JUICE’s instruments include detectors to study the radiation and plasma environment surrounding Jupiter. It will provide insights into the interactions between Jupiter’s magnetic field and the charged particles that populate its environment.

Which space agencies and institutions are involved in the JUICE Mission?
European Space Agency (ESA):
ESA is leading the JUICE mission. It is responsible for the mission’s overall management, coordination, and funding.
NASA
NASA’s contributions include the UVS instrument and parts for RIME (Radar for Icy Moon Exploration) and PEP (Particle Environment Package). However, NASA is not a direct partner in the JUICE mission.
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA):
JAXA has contributed to the development of RPWI (Radio and Plasma Wave Investigation), GALA (Ganymede Laser Altimeter), and PEP.
Israel Space Agency (ISA):
The ISA has supplied hardware for the 3GM instrument, which is part of the JUICE mission.
In addition to these agencies, the mission involves a collaboration of 18 institutions and 83 companies from 23 different countries.
What are the potential discoveries expected from the JUICE Mission?
Habitability of Icy Moons:
The mission seeks to understand the conditions that could support liquid water oceans beneath the surfaces of Ganymede, Europa, and Callisto.
Characterization of Gas Giant and Magnetosphere:
JUICE Jupiter Mission will study Jupiter’s gas giant characteristics and its magnetosphere. And by studying the gas giant’s structure, composition, and magnetic field, scientists hope to gain insights into the planet’s formation and evolution.
Understanding Ganymede’s Magnetic Field:
JUICE will extensively study Ganymede’s magnetic field and its interaction with Jupiter’s magnetic field to uncover the dynamics and processes behind the generation of Ganymede’s magnetic field.
Geological and Surface Features:
The mission will provide insights into the moon’s geological history, such as tectonic activity, cryovolcanism, and the presence of subsurface water.
Astrobiology and Origins of Life:
The mission will investigate the conditions that may have led to the emergence of habitable environments and assess the possibilities for life beyond Earth.
After studying these, JUICE will be capable of understanding the Jovian system, the habitability of icy moons, and the broader field of astrobiology.
How does radiation pose a risk to the JUICE spacecraft?
Radiation poses a risk to the JUICE spacecraft in several ways. Here are a few key points:
- Radiation can damage the spacecraft’s electronics.
- Data transfer disruption.
- Degradation of spacecraft’s parts.