Time and gravity are two of the most fascinating concepts in physics. While our everyday experience of time is straightforward, its scientific definition is much more complex and intertwined with other physical phenomena. One such relationship is the effect of gravity on time, as predicted by Einstein’s theory of General Relativity. According to this theory, time can slow down in strong gravitational fields, a phenomenon known as time dilation. This has been confirmed through experiments and is also a key component of technologies such as GPS. In this article, we will delve into the relationship between gravity and time, exploring the science behind time dilation and its implications.
Does Gravity Slow Down Time
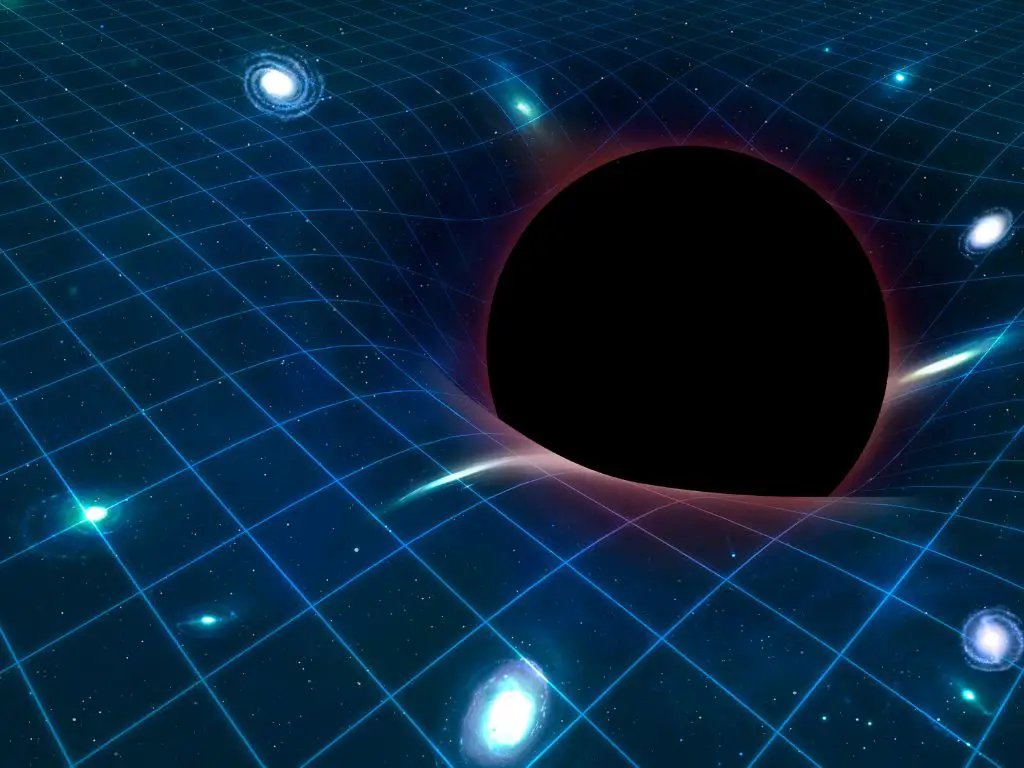
Yes, according to Einstein’s theory of General Relativity, gravity can slow down time. When an object moves near a massive object such as a star or a black hole, its clock will run more slowly compared to a clock far away from the massive object, a phenomenon known as time dilation. This effect has been confirmed by experiments and is also used in the Global Positioning System (GPS). However, it’s important to note that time is not a single, absolute entity and its pace can depend on the observer’s location and relative motion.
What is Time according to Science
In science, time is not considered to be a fixed, absolute entity that moves at the same pace everywhere. Instead, scientists view time as relative, meaning it depends on the observer’s location and motion relative to what is being measured. Time cannot be directly measured, but is instead inferred through the measurement of regular events, such as heartbeats or the movement of a pendulum. This process of counting regular events is referred to as a clock.
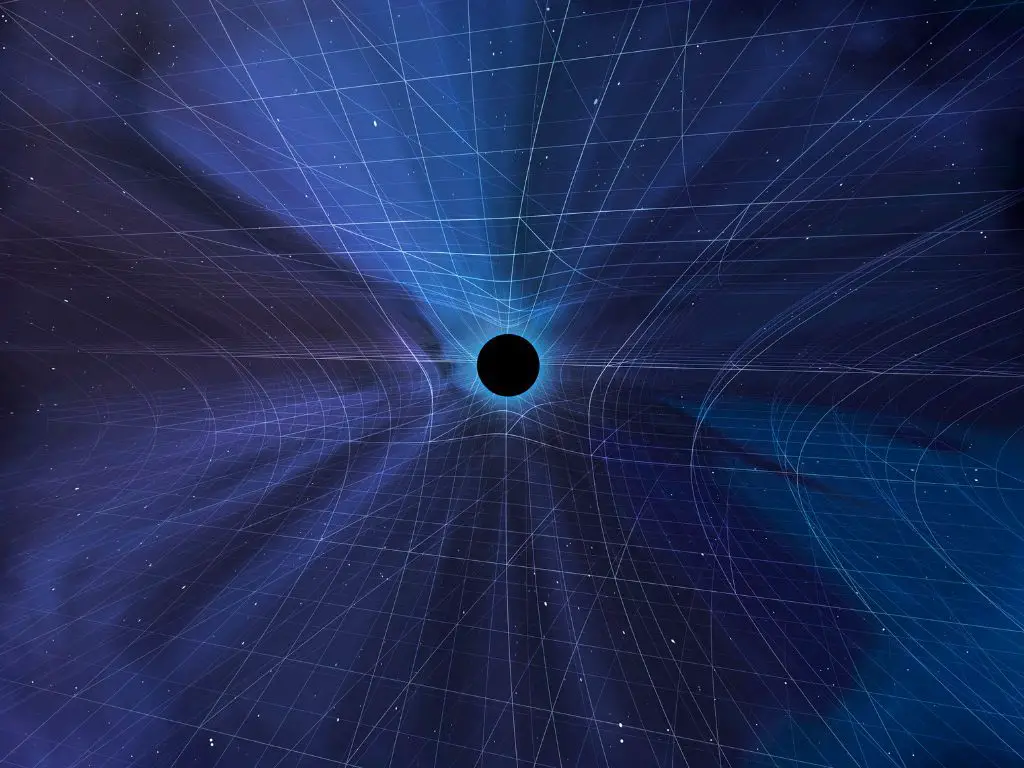
It’s important to note that the pace of time can appear to change based on the observer’s location and relative motion. For example, if you were observing time near a black hole, you would observe that time is moving more slowly than if you were far away from the black hole. This doesn’t mean that the clock near the black hole is running slower, but rather that your measurement of time is affected by your location and motion relative to the clock and the black hole.
Additionally, it’s crucial to understand that time is not a single, monolithic entity that ticks along at the same pace everywhere. Instead, the pace of time can vary depending on the observer’s location and relative motion, and even the presence of objects such as black holes.
It’s worth noting that there isn’t a definitive answer to why time works this way. Reality is what it is and may not conform to our preconceived ideas or what we would like it to be.
Time is a multifaceted concept that is still not fully understood by scientists and can have different interpretations based on the context and the field of study.
General Relativity and Time Dilation
The idea that the pace of time can change based on the observer’s location and relative motion is a cornerstone of Einstein’s theory of General Relativity. In this theory, gravity is seen as a curvature of spacetime, caused by massive objects such as stars and black holes. When an object moves near a massive object, its clock will run more slowly compared to a clock far away from the massive object, a phenomenon known as time dilation.
GPS and Time Dilation
The time dilation effect of General Relativity is used in the Global Positioning System (GPS), where satellite clocks run faster than clocks on the ground. This effect must be taken into account to ensure accurate navigation with GPS.
Quantum Mechanics and Time
Another important aspect of time in physics is its role in the field of quantum mechanics. In quantum mechanics, time is considered to be a parameter rather than an absolute quantity. This means that time is not a fundamental, irreducible aspect of reality, but instead a tool used to describe the evolution of a quantum system.
Time Perception
Another interesting aspect of time is how we perceive it. Time perception is a complex and subjective phenomenon, as our experience of time can change based on a variety of factors, such as stress, aging, or even the presence of other people.
In conclusion, time is not absolute in science, and the pace at which time appears to move can change based on the observer’s location and motion relative to what is being measured. It’s important to understand that time is not a single entity that moves at the same pace everywhere, and that the pace of time can be affected by various forces and objects in the universe.