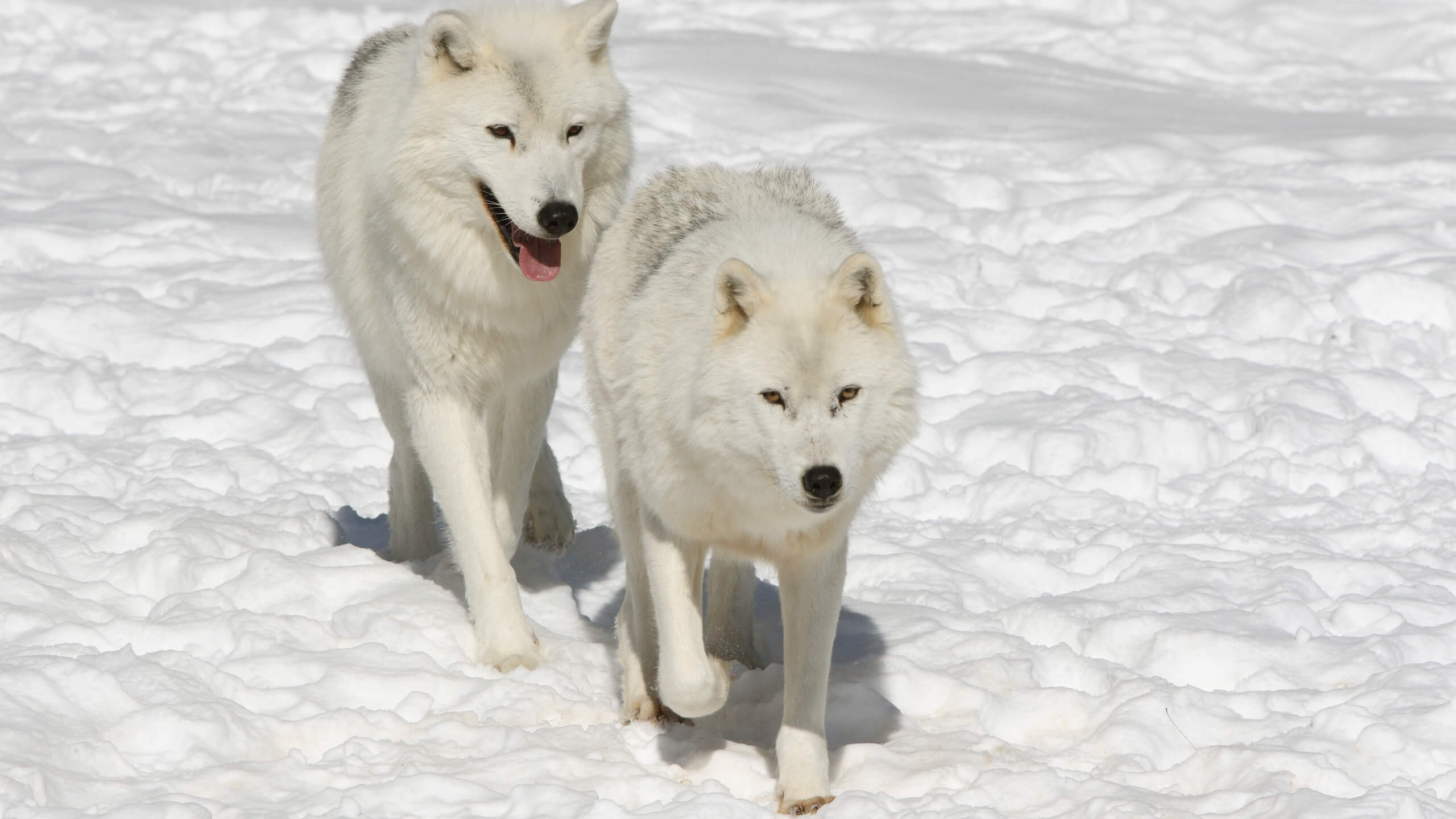
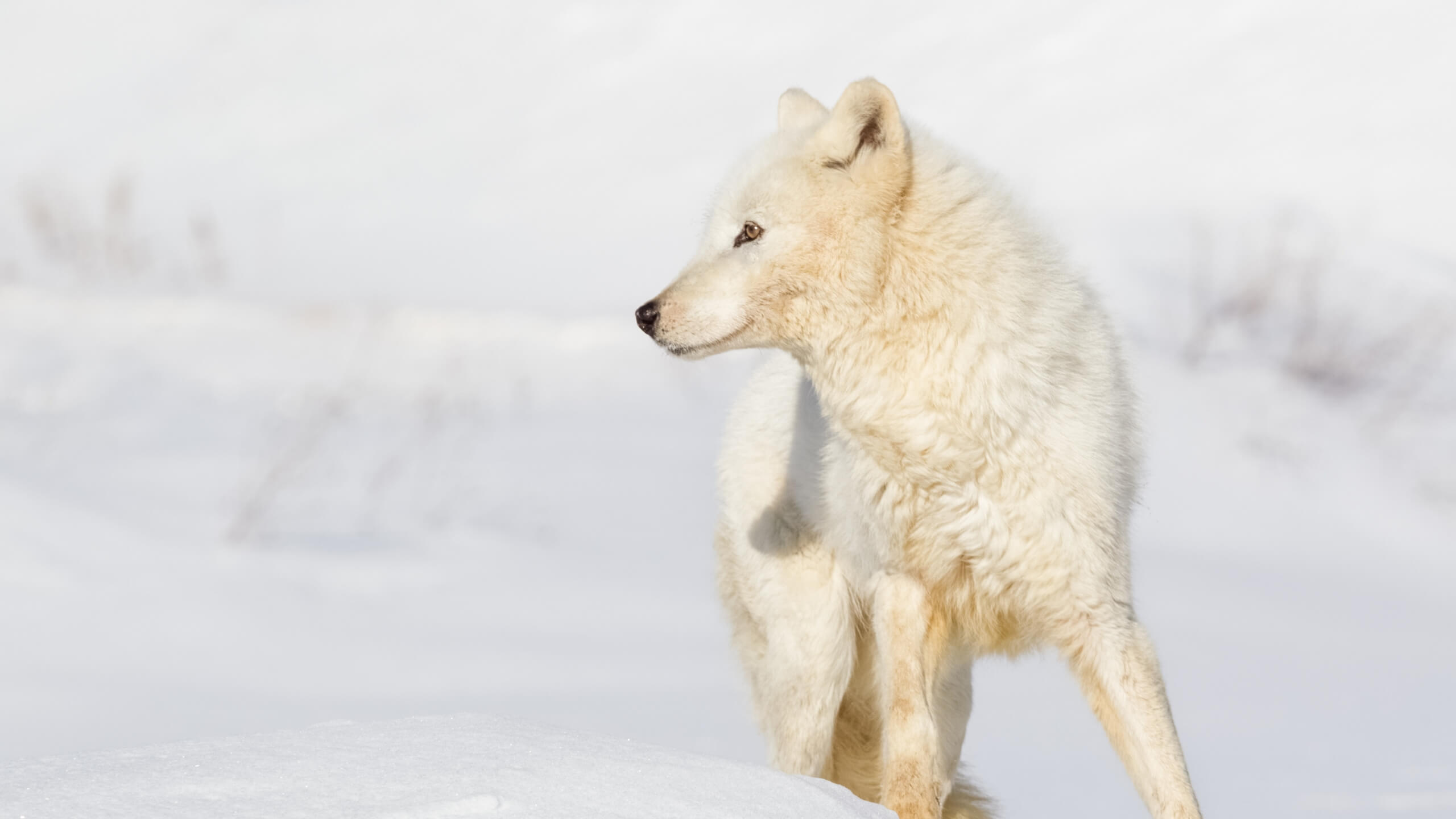
The Arctic wolf is a subspecies of gray wolf that is also known as polar wolf or white wolf. It is indigenous to the high Arctic tundra regions of North America and Greenland. Arctic wolves are not endangered because of their isolated habitat where human activities are inconsiderable.
They are also well-adapted to the extreme climate conditions of Arctic tundra where they do well. Their current population is estimated at 200,000 individuals, and their conservation status on the IUCN Red is Least Concern.
Despite that, Arctic wolves are still facing threats like climate change and some human activities that may cause damage to them. Here we gathered information about why Arctic wolves are endangered and what are the threats they are facing to their survival.
Why Are Arctic Wolves Endangered?
Arctic wolves are not endangered because of their isolated habitat. Their current conservation status on the IUCN Red List is Least Concern, which is the lower rank of endangerment. However, they are still facing many threats to their survival.
Also Read: How many Orcas are left in the world?
The major threat they are facing is climate change. Climate change is causing the melting of sea ice, changes in the ecosystem, and reduction in their prey species. From 1997, a decline was observed in the population of Arctic Wolves and their prey (muskoxen and Arctic hares) because of unfavorable climate conditions in the summer. However, their populations recovered when the climate condition became normal after four years.
Another major threat Arctic wolves are facing is industrial development, oil drilling, and other human activities in their habitat range. Increasing numbers of mines, construction of roads and highways, and spreading pipelines encroach on their territories and also disturb their food supply. Disruption in food supply directly impacts their reproduction and survival rates.
What Are The Threats To The Arctic Wolves?
Arctic wolves are not currently classified as endangered. Very little is known about Arctic wolves because of the extreme climate conditions of their habitat. Because of their isolated habitat, they may not face the threats of hunting or habitat destruction. However, they are still facing threats that other subspecies of wolves do in certain regions. The following are some threats that Arctic wolves may be facing:
Climate Change impact on Arctic Wolves
Like most other animal species, climate change is a major threat to Arctic Wolves. Because of global warming and climate change, the Arctic region is experiencing melting of sea ice and glaciers and changing ecosystems. These changes can disrupt the hunting and reproductive patterns of the Arctic wolves and lead to a lower survival rate and a decline in their population.
Human Activities
Human activities in their habitat range, such as oil drilling, mining, road and highway construction, and the spreading of pipelines can disrupt their food supply. Other human activities like illegal hunting for their fur and trophy hunting can also have harmful effects on their populations.
Reduction In Prey
The primary prey of Arctic wolves are muskoxen, Arctic hares, and caribou. Climate change, habitat loss, and other activities like overhunting can cause a decline in the population of these animals and can disrupt the food supply of Arctic wolves. Low food supply directly affects their reproduction rate and population.
Arctic wolves Habitat Loss
Climate change and human activities can lead to the destruction of Arctic wolves habitat. Sea ice and glaciers are melting because of global warming which is causing change in their ecosystem. Human intrusion in their habitat for oil drilling and mining is destroying their habitat. All these activities together can change their reproductive and hunting patterns and can pose a threat to their survival.
Diseases And Predation
Like other subspecies of wolves, Arctic wolves can also be susceptible to diseases and parasites that can impact their populations. Besides that, increased competition with other predators and predation from other species, like polar bears and other wolves, can put additional pressure on their numbers.