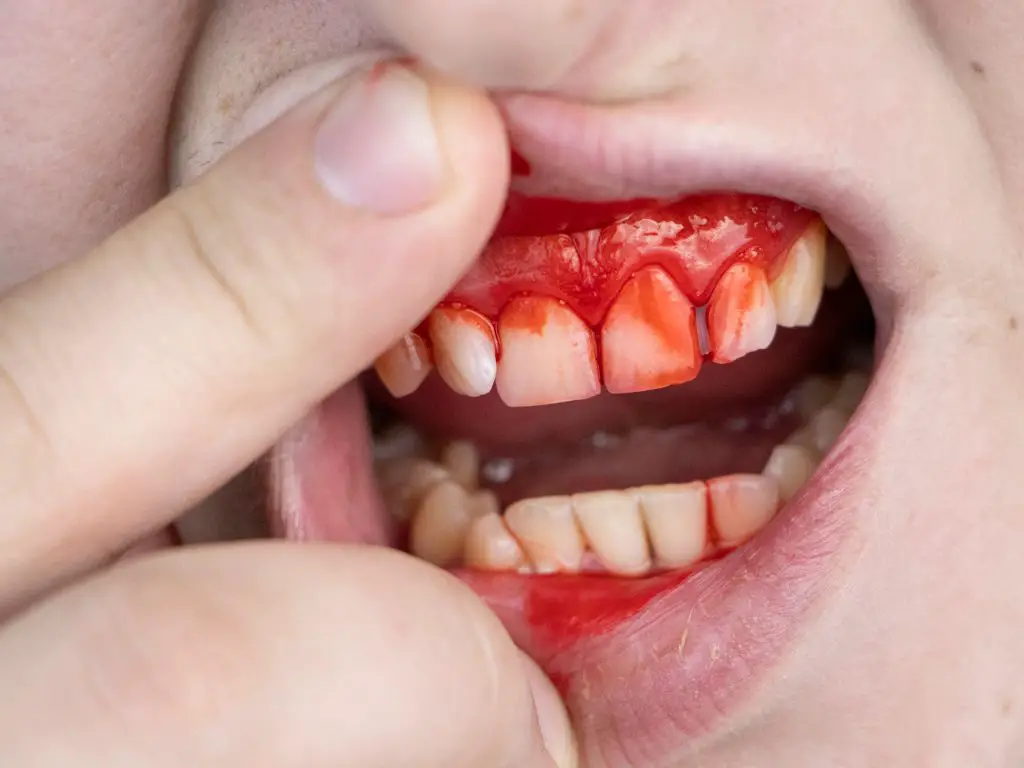
Gum disease can have life-threatening consequences if left untreated. It is caused by an accumulation of plaque and bacteria on the surfaces of teeth, leading to inflammation and infection in the gums. If not treated promptly, gum disease can cause extensive damage to your oral health as well as other parts of your body.
The most common symptom of gum disease is bleeding gums when brushing or flossing; however, it may also manifest itself through bad breath or receding gums. In more severe cases, bone loss around teeth may occur which leads to tooth mobility and eventually loss altogether. Additionally, individuals with advanced stages of periodontal (gum) diseases are at higher risk for developing systemic illnesses such as cardiovascular diseases due to increased bacterial load in their bloodstreams from infected mouth tissues entering circulation systemically via saliva flow into digestive tract.

Gum disease that can kill you
While gum disease is not typically considered to be life-threatening, it can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Here are a few types of gum disease that can have serious consequences:
- Chronic periodontitis: This is the most common form of gum disease, and it is characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It is caused by the build-up of plaque and tartar, and it can lead to bone loss, tooth loss, and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and other health problems.
- Aggressive periodontitis: This type of gum disease is characterized by rapid bone loss and tooth loss, and it is often seen in younger people. It is caused by bacteria that produce toxins that damage the gums and supporting structures of the teeth.
- Necrotizing periodontal disease: This is a rare and severe form of gum disease that is characterized by the death of gum tissue, bone, and other supporting structures of the teeth. It is often seen in people with compromised immune systems, such as HIV/AIDS patients, and it can be life-threatening if left untreated.
- Abscessed teeth: A dental abscess is a pocket of pus that forms at the end of a tooth or in the gums. It is caused by a bacterial infection, and it can be extremely painful. If left untreated, an abscessed tooth can spread the infection to other parts of the body, potentially leading to serious complications.
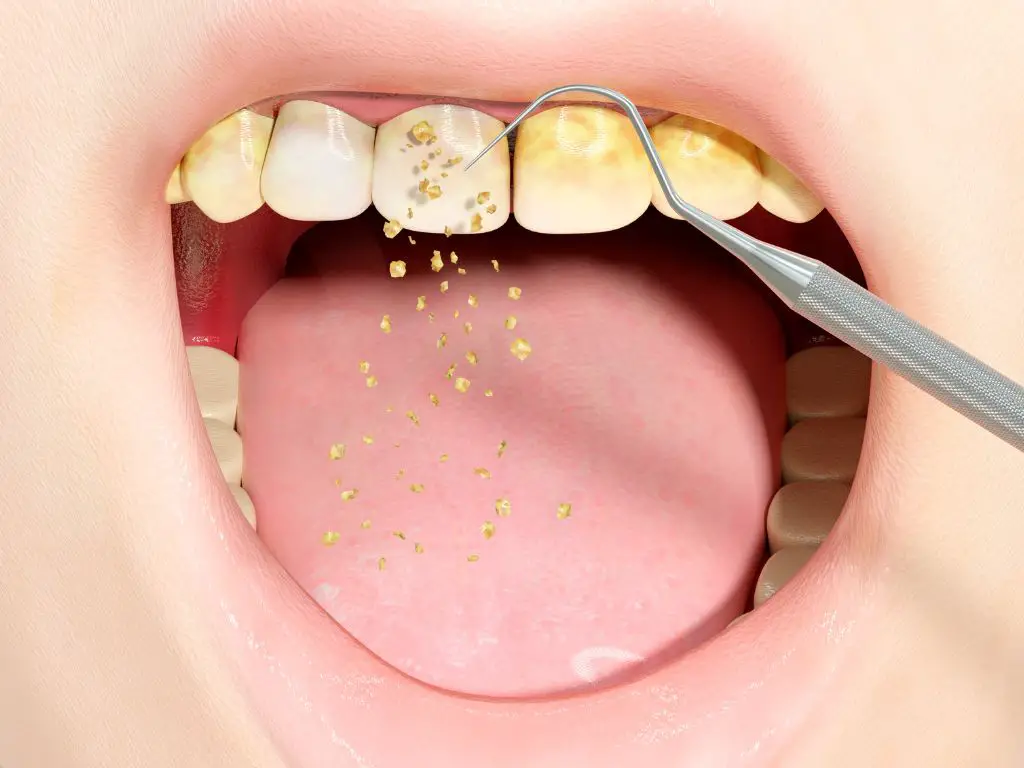
It is important to practice good oral hygiene and visit your dentist regularly to prevent gum disease and other oral health problems. If you are experiencing any symptoms of gum disease, such as bleeding gums, red or swollen gums, or tooth sensitivity, it is important to see your dentist as soon as possible to get proper treatment.
What happens if gum disease is left untreated?
If gum disease is left untreated, it can progress and become more severe, leading to a range of negative effects on your oral health and overall well-being. Some potential complications of untreated gum disease include:
- Tooth loss: Gum disease can cause the gums to recede, exposing the roots of the teeth and making them vulnerable to decay and infection. It can also lead to bone loss, which can weaken the supporting structures of the teeth and make them more prone to falling out.
- Cardiovascular disease: Studies have shown that there may be a link between gum disease and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, such as heart attack and stroke. The inflammation and infection associated with gum disease may contribute to the development of these conditions.
- Respiratory problems: Bacteria from gum disease can enter the bloodstream and travel to the lungs, where it can contribute to the development of respiratory problems such as pneumonia.
- Pregnancy complications: Gum disease has been linked to an increased risk of complications during pregnancy, such as preterm birth and low birth weight.
- Other health problems: Gum disease has been associated with a range of other health problems, including diabetes, kidney disease, and osteoporosis.
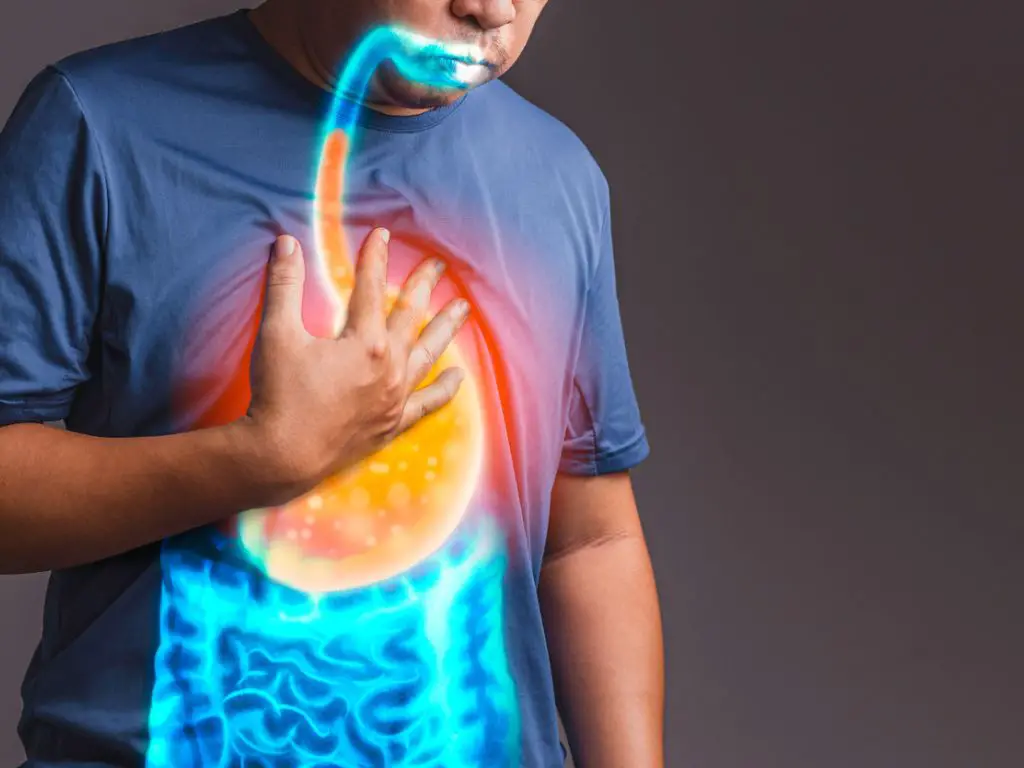
How long does it take for gum disease to kill you
Gum disease is not fatal on its own, however it can lead to more serious conditions such as heart attack or stroke if left unchecked for too long. So how long does it take for gum disease to kill you?
🔬 Subscribe to SciMail
Get the latest science discoveries straight to your inbox!
The answer depends on several factors including the severity of the condition and how quickly treatment is sought out. In general, severe cases of advanced gum diseases like periodontitis may require extensive treatments in order to be effectively managed over time. Without proper care from dental professionals these conditions could eventually become life-threatening depending upon their progression rate and other individual circumstances.
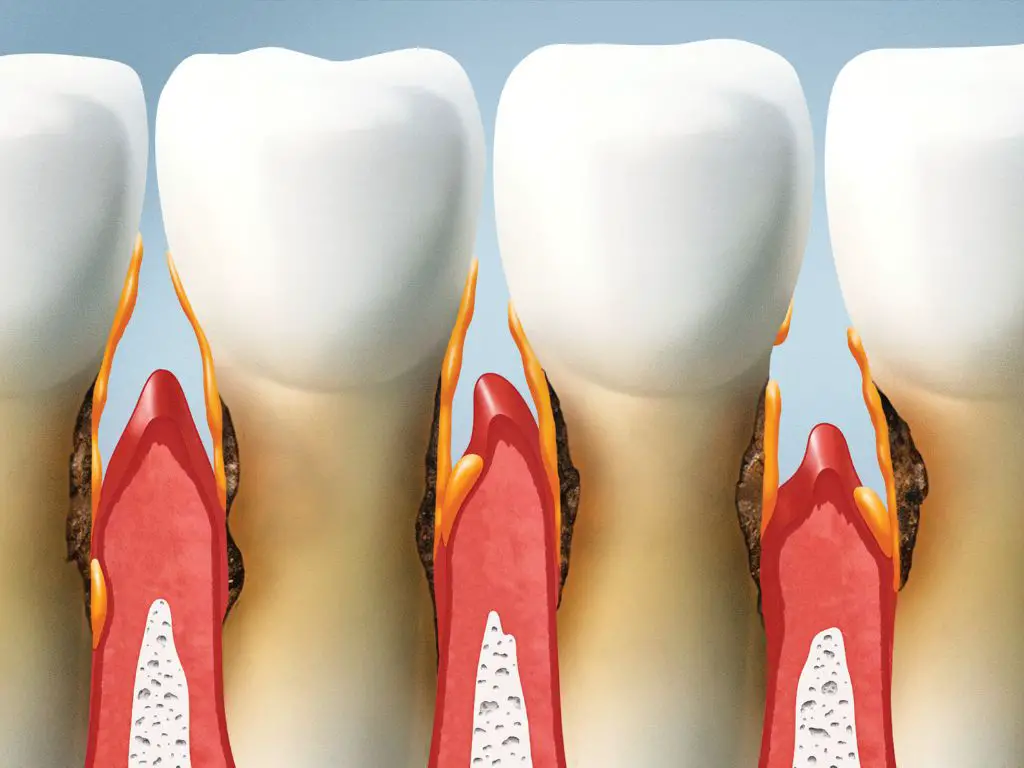
For example, an individual with diabetes might experience faster deterioration due to weakened immunity levels which could put them at greater risk for developing complications related to their oral health issues such as infection or abscesses in extreme cases where timely intervention was not taken into account priorly by medical professionals involved in patient’s care plan management process.
How long can you live with gum disease
It is not possible to determine exactly how long someone can live with gum disease, as it depends on various factors such as the severity of the disease, the individual’s overall health and immune system, and the effectiveness of their treatment.
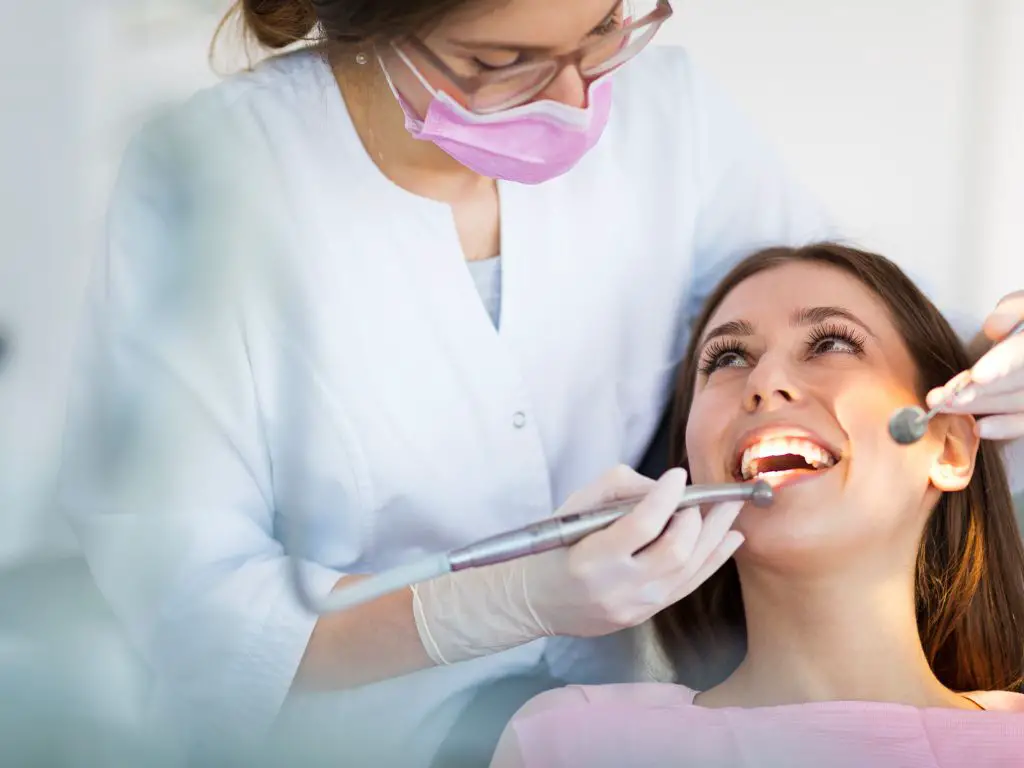
It’s important that individuals who are diagnosed with any form of gum disease seek professional help immediately so they don’t suffer further consequences down the line; this includes regular visits with a dentist every six months (or more often depending on your doctor’s recommendation). Additionally maintaining good overall hygiene habits like brushing twice daily along with flossing regularly will go a long way towards keeping your mouth healthy while minimizing potential risks associated with poor dental hygiene practices.

Leave a Reply