Saturn is the sixth planet in the solar system and the second largest after Jupiter. It is composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. This made Saturn into a gas giant with no solid surface and gravity is measured where atmospheric pressure is the same as Earth’s sea level pressure. Saturn spins so fast that gravity varies between the poles and the equator.
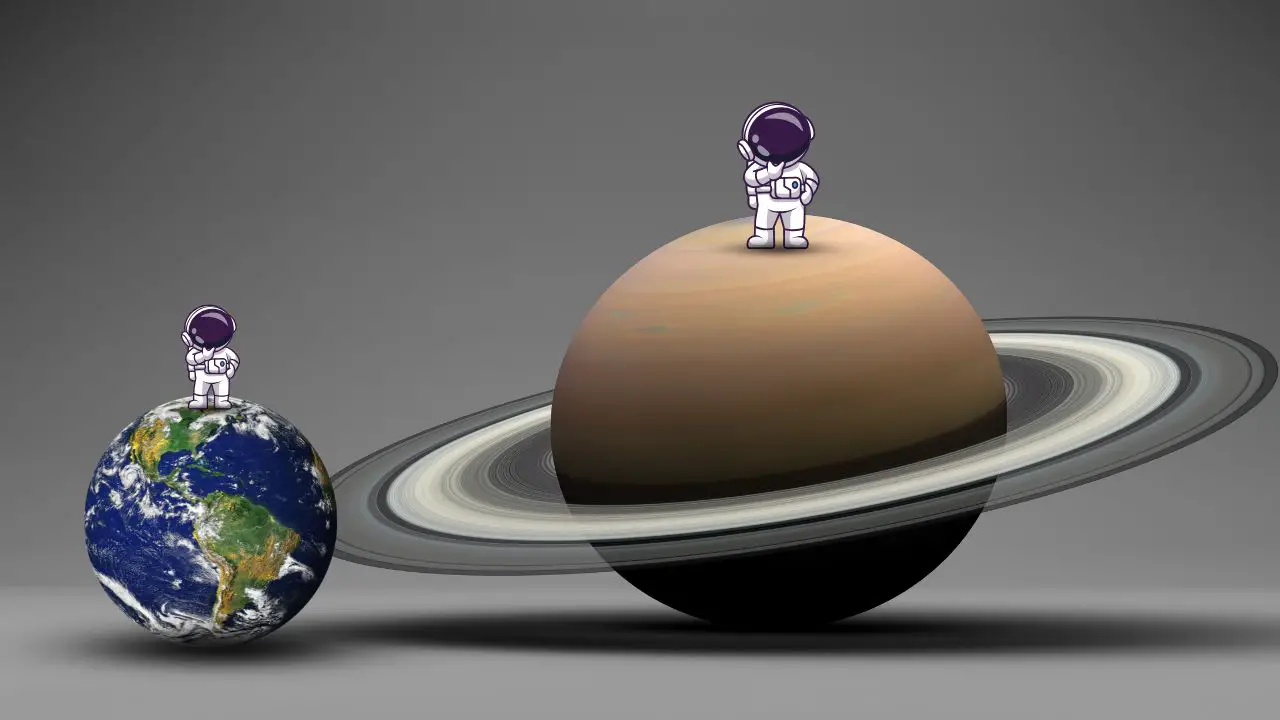
The centrifugal force from this spinning makes objects feel lighter at the equator than at the poles. Its equatorial diameter is approximately 119,300 kilometers (74,130 miles), making Saturn 9.5 times wider than Earth. Saturn is less dense than water. This means it can float in a large bathtub. With a gravity force of 10.44 m/s, Saturn’s gravity is 1.08 times greater than Earth’s.
A person weighing 100 pounds on Earth would weigh about 108 pounds on Saturn. Unlike Earth, Saturn does not have a solid surface. Its “surface” is determined by pressures on Earth that are equivalent to sea level. Additionally, its rapid rotation causes slight shifts in gravity between the poles and the equator making it feel lighter at the poles.
How strong is the gravity on Saturn?

Saturn’s gravity is about 10.44 meters per second squared (m/s²), which makes it approximately 1.08 times stronger than Earth’s gravity of 9.806 m/s². This means that an object weighing 100 kilograms on Earth would feel like it weighs around 108 kilograms on Saturn. Though this increase in weight is less dramatic than on Jupiter, Saturn still has a significant gravitational pull.
Also Read: Can you walk on Saturn’s rings?
Saturn has an overall low density and strength of gravity from its mass of about 5.6834 x 10²⁶ kilograms, around 95 times that of the Earth. Saturn has around a 9.14 times larger radius with about 58,232 kilometers. Like Jupiter, Saturn is also a gas giant composed mainly of hydrogen and helium.
However, its mean density is just 0.687 g/cm³, much lower than Earth’s 5.51 g/cm³, making Saturn’s density about 12.5% that of Earth’s. Saturn’s gaseous composition compared to Earth’s rocky structure contributes to this low density.
Although the gravity pull of Saturn is considerably lower than that of Jupiter, its powerful gravitational force is strong enough not only to maintain its large rings but also many moons. It is also very difficult for spacecraft to orbit around Saturn mainly due to its strong gravity. Saturn has a big size and a strong gravitational force that affects the nearby objects which makes missions on Saturn hard.
What is Saturn’s gravitational field strength?

The gravitational force on Saturn is about 10.44 meters per second squared (m/s² ) which means if you drop an object, it would accelerate toward the surface at this rate. For example, a 100-kilogram person on Earth would have to weigh about 108 kilograms on Saturn due to the stronger gravitational pull. Likewise, when Earth has a gravity of 9.81 m/s² so if you imagine dropping a ball on Saturn the same one would drop at a faster rate at 10.44 m/s² due to the stronger pull of gravity from Saturn, thus hitting the ground slightly harder.
Also Read: When will Saturn’s rings disappear?
Is Saturn’s Gravity Similar to Earth’s?

Saturn’s gravity is similar to the Earth’s but slightly different. Saturn has about 10.44 m/s² strength of gravity, compared to the Earth’s 9.81 m/s² this means that the strength of Saturn’s gravity is approximately 1.08 times stronger than Earth’s. This means objects on Saturn would experience slightly more force.
🔬 Subscribe to SciMail
Get the latest science discoveries straight to your inbox!
For example, if you dropped a rock on Saturn it would drop slightly faster than on Earth due to the comparatively stronger pull of Saturn’s gravity which is 10.44 m/s² compared to 9.81 m/s² on Earth. This extra gravity affects the rate at which the objects fall to the surface.
How Does Saturn’s Gravity Influence Its Rings and Moons?

Saturn’s gravity plays a key role in the formation of its rings and moons. Its powerful gravity keeps the rings in place and creates gaps in the rings through a process called orbital resonance. Where the gravity of moons like Mimas affects the ring particles and creates patterns
Saturn’s gravity also controls the orbits of more than 80 moons, including large moons Titan and Enceladus. Some small moons, also known as “The Shepherd Moon” help maintain the ring’s structure by acting as a stabilizer. Keep the particles aligned and create space without Saturn’s strong gravity scattering or disturbing the moons in the rings.
Also Read: Can You Walk On Saturn’s Rings?
Can Saturn’s Gravity Impact Other Planets in the Solar System?
Yes, Saturn’s gravitational pull can affect other planets in the solar system, but its influence is generally limited by the vast distances between the planets. Saturn’s strong gravity affects objects such as rings and moons within its own system.
But because it has a huge mass. Saturn therefore has a gravitational effect on nearby objects. including asteroids and comets and to some extent with other planets. Especially when they are in close alignment with each other or when their orbits bring another planet close.
For example, Saturn helps shape the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Therefore, the orbit of an asteroid is affected by the combined gravitational pull. Saturn’s gravity also plays a role in stabilizing the long-term orbits of the outer planets such as Uranus and Neptune. Although the effect is small compared to the effect of s, Saturn’s overall gravitational effect on other planets is less.
Does Saturn’s Gravity Affect Space Missions?

Yes, Saturn’s gravity affects space missions. Spacecraft could use Saturn’s strong gravity to “gravity assisted” vehicles, where they get speed and change direction without using extra fuel. This allowed the Voyager and Cassini missions to further explore space.
However, Saturn’s gravitational pull might make things difficult. So while Saturn’s gravity is helpful, it must be managed carefully for the mission to succeed. Spacecraft need to avoid being pulled too close to the planet or its moons, and navigating through or near its rings requires careful planning to avoid debris.


Leave a Reply