The artificial intelligence systems designed to physically interact with and learn from their environment through technologies like sensors, motors, actuators, and machine learning are known as embodied AI. Embodied AI operates in the physical and real world, able to act, learn, and perceive from its environment. Here, we gathered information about embodied AI, its key features, elements, history, and some examples.
What Is Embodied AI?
Embodied AI is a relatively new term, which refers to artificial intelligence systems that can physically interact with and learn from their surroundings through a suite of technologies. Unlike Cognitive AI (which learns from data sources and what people say about a thing) embodied AI has the ability to learn from its experience in physical surroundings. It operates in a direction that is more related to a reflex rather than a concept.
Also read: Can AI outperform human intelligence?
The inspiration for embodied AI has been taken from biological systems, like animals and humans, which use their physical bodies to gather information, navigate, and adapt to changes. In embodied AI, perception (seeing and sensing), action (moving and manipulating), and learning (adapting and improving) have been combined to perform tasks.
Key Features Of Embodied AI Systems
The key features of embodied AI are:
- Physical Interaction: It physically interacts with the surroundings through touch, movement, and manipulation.
- Sensorimotor Integration: To perceive data and to act, embodied AI uses sensors (microphone and camera) and actuators (motors).
- Learning from experience: To improve its performance over time, embodied AI uses machine learning algorithms (including reinforcement learning).
- Adaptive behavior: As inspired by biological systems, embodied AI can adapt to unpredictable conditions, much like humans and animals.
Elements Of Embodied AI Systems
Embodied AI is applied to any AI system that interacts with the surroundings and learns. Many elements are included in more capable systems over different dimensions of the embodiment. However, some of the most important are:
- World Model: A world model is the internal representation of an AI system about its environment and self. It is the key element of embodied AI systems, which helps them to make smart and safe decisions while achieving their goals. Nvidia’s Omniverse platform is an example that uses simulated and physical-based world models to train robotic and self-driving vehicles embodied AI systems to make them more capable and reliable.
- Sensors: Sensors in an embodied AI system gather information about the surroundings and help to create and update the world model.
- Actuators: Actuators are movement-producing devices in AI systems that convert energy into mechanical motion. These devices allow the embodied AI system to interact or change with its environment, move around, or adjust itself in that environment.
- Coordination: Coordination means how the AI systems collaborate with other systems and people to achieve goals.
- Approach: Approach means the strategy an AI system uses to learn from its environment. For example, a policy-based approach is used in reinforcement learning to achieve the highest possible reward. Another example is active inference, which aims to reduce uncertainty (the difference between reality and its expectations). This process reduces free energy, which refers to uncertainty or prediction errors.
History Of Embodied AI

🔬 Subscribe to SciMail
Get the latest science discoveries straight to your inbox!
Embodied AI is a relatively new term, but the basic concept of adaptive control system dates back to 1788 with the invention of centrifugal governor by James Watt. It was a feedback system used to adjust the flow of fuel into the steam engine.
In the 1940s, William Grey Walter invented the cybernetic tortoise in the U.K. It was the earliest robot that could interact with its environment. In the 1960s, Stanford Research Institute developed Shakey the robot, which was capable of learning, planning, and reasoning.
In 1973, researchers in Japan developed the first full-scale humanoid robot, WABOT-1. It could walk, talk, and interact with its environment.
In the 1980s, behavior-based robotics emerged with a great focus on real-time and quick responses to its environment. In the 1990s, theories about embodied cognition emphasized that learning happens through physical interactions. It inspired humanoid robots like ASIMO developed by Honda.
In the 2010s, further advances in deep learning and simulations enabled the development of smarter adaptive systems. It led to applications in self-driving cars, healthcare robots, and smart devices. Today, embodied AI is improving towards human-like intelligence and interactions with the environment.
In 2024, The Chinese company RobotEra introduced a humanoid robot named STAR1, which is now the fastest bipedal robot, reaching speeds of 8 mph. STAR1 is 5 feet 7 inches tall and weighs 143 pounds. It uses advanced AI and powerful motors to move quickly.
What Are examples of embodied AI?
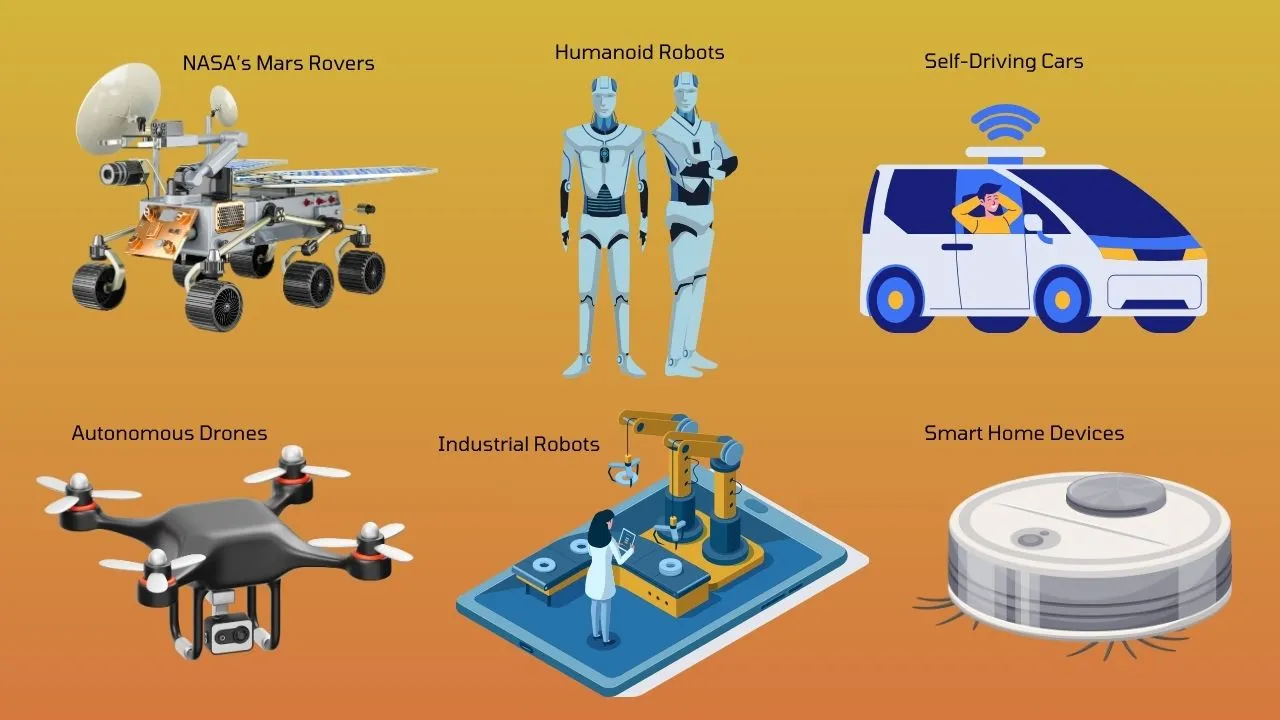
Some examples of embodied AI are:
- NASA’s Mars Rovers: NASA’s Perseverance and Curiosity rovers are designed to explore and collect information from Mars.
- Humanoid robots: Humanoid robots like Honda’s ASIMO are designed for assistance, that can walk, climb stairs, and interact with humans. Another example is the Pepper robot of Softbank, which is a social robot that can engage in conversations. They are used as receptionists in offices and in homes in Japan.
- Self-Driving Cars: Self-driving cars use sensors and AI for road navigation, obstacle detection, and making driving decisions.
- Autonomous Drones: They are autonomous flying machines used for surveillance, mapping, and deliveries.
- Assistive and Medical Robots: Assistive and medical robots using embodied AI include, Ekso Bionics (a wearable device for disabled individuals to regain mobility) and da Vinci Surgical Systems (assisting surgeons during operations).
- Industrial Robots: Collaborative robots (also known as Cobots) work together with humans in factories to assemble products.
- Smart Home Devices: Simplified forms of embodied AI smart home devices are robotic vacuum cleaners (Roomba) and lawnmowers.


Leave a Reply