There are growing rumors about an asteroid colliding with Earth in recent years. Asteroid crashes are a big worry for both scientists and the public, as they can be disastrous for the planet. It is important to distinguish reality from fiction. A variety of science fiction films and apocalypse notions are increasing the concern. Get ready to address the urgent question: Is an asteroid heading towards Earth?
Is there an asteroid headed towards earth?
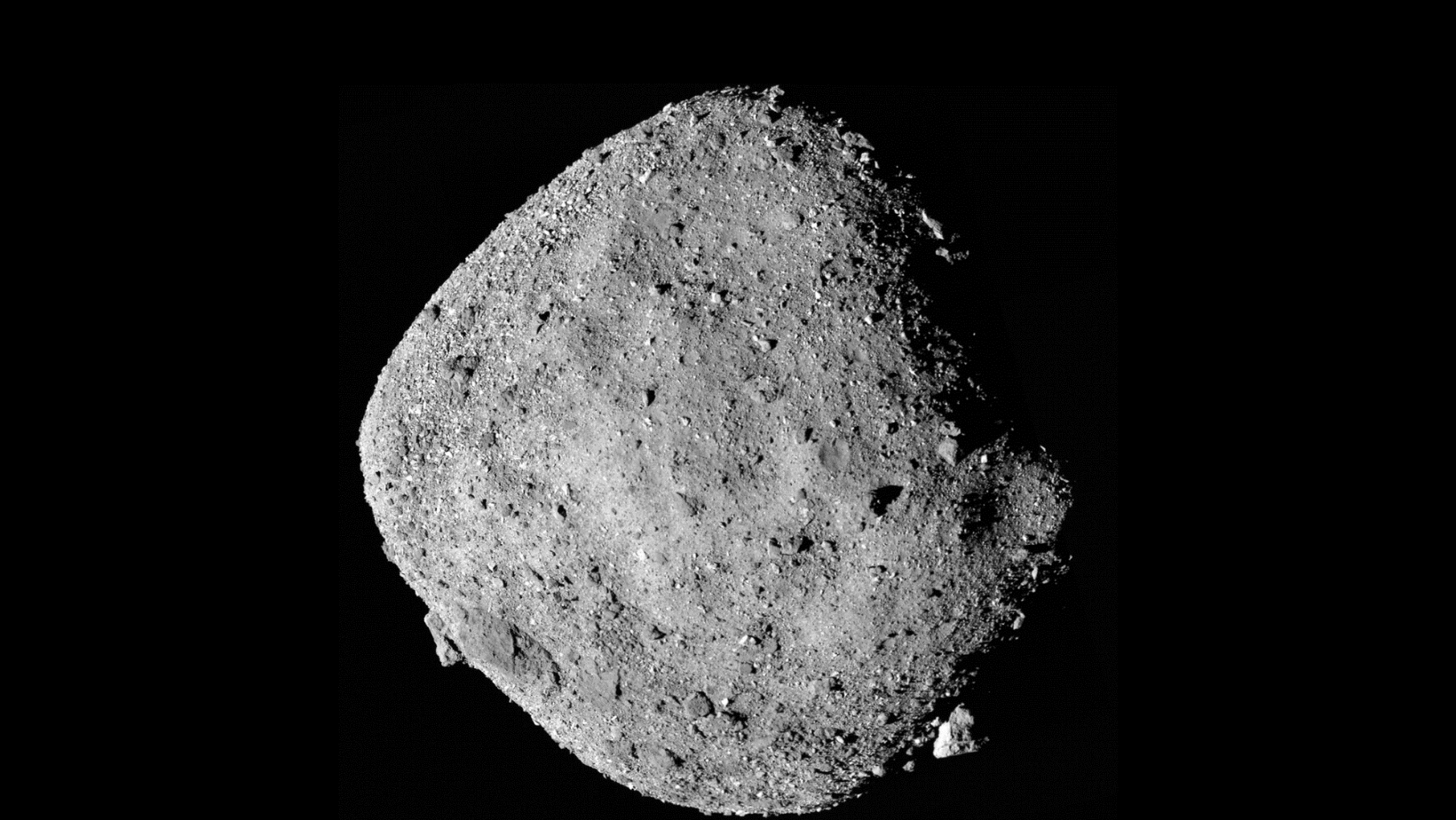
Yes, The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has issued a warning on a large asteroid that is on its way to Earth. They assume it to be around the size of a very tall building. The enormous carbon-based space rock is named “Bennu,” and is 210 meters broad.
It would release an enormous 1,200 Mt of energy if it hits the earth’s surface. This is equal to the energy produced by 24 nuclear bombs. There is no confirmed date for the collision.

Which asteroid is coming towards Earth?
The asteroid coming towards earth is Bennu, which is approximately 510 meters wide. According to NASA, it is a giant slab of carbon that can hit the earth anytime soon. Other interesting asteroids are being watched and tracked carefully by experts. To safeguard the security and wellbeing of our planet, they are always trying to develop detection and tracking technologies.
The science behind asteroid detection
The detection of asteroids can be done in many ways. An important area of astronomical research is the discovery of asteroids. It comprises locating and monitoring asteroids that might pose a danger to Earth. Using telescopes and observatories is the first step in the discovery of asteroids. Scientists can monitor asteroids by studying the data collected.
Spectroscopy is also a vital tool in the search for asteroids. This entails examining the light spectrum radiated by asteroids to observe their composition. Recently, researchers are employing modern methods to detect asteroids such as radars.
The impact of an asteroid collision
Both on a local and a global scale, the impact of an asteroid strike can be disastrous. Asteroid collisions with the Earth result in the release of enormous amounts of energy.
🔬 Subscribe to SciMail
Get the latest science discoveries straight to your inbox!
| Asteroid Size | Potential Impact |
| Smaller than about 25m (about 82 feet) | Little to no harm as they burn up on the earth. |
| Larger than 25m but smaller than 1 Km | Can cause local damage to the affected region. |
| Larger than one to two kilometers | Could have global effects. |
| Larger than 2 kilometres | Can cause immense destruction. |

Preparing for a potential asteroid threat
It is necessary to take precautions, though the possibility of an asteroid hitting earth is low. The most important thing is to have an early-warning system that can find potentially dangerous asteroids. Astronomers, scientists, and global space organizations will need to work together on this.
We must also create plans to lessen the effects of asteroids. We can use kinetic impactors or gravity tractors to steer an asteroid away from Earth. Also, it is crucial to inform and educate the people about the hazards and precautions to take. Finally, emergency response plans must be put in place.
When was the last asteroid to hit Earth?
The Chelyabinsk asteroid was the one that hit earth in 2013 and had a huge impact. At a speed of around 70,000 kilometres per hour, the asteroid crashed into the atmosphere of Earth. It released an energy equivalent to 500,000 metric tonnes of TNT being detonated. Satellites, as well as many witnesses and cameras, saw the asteroid’s smoke trail.
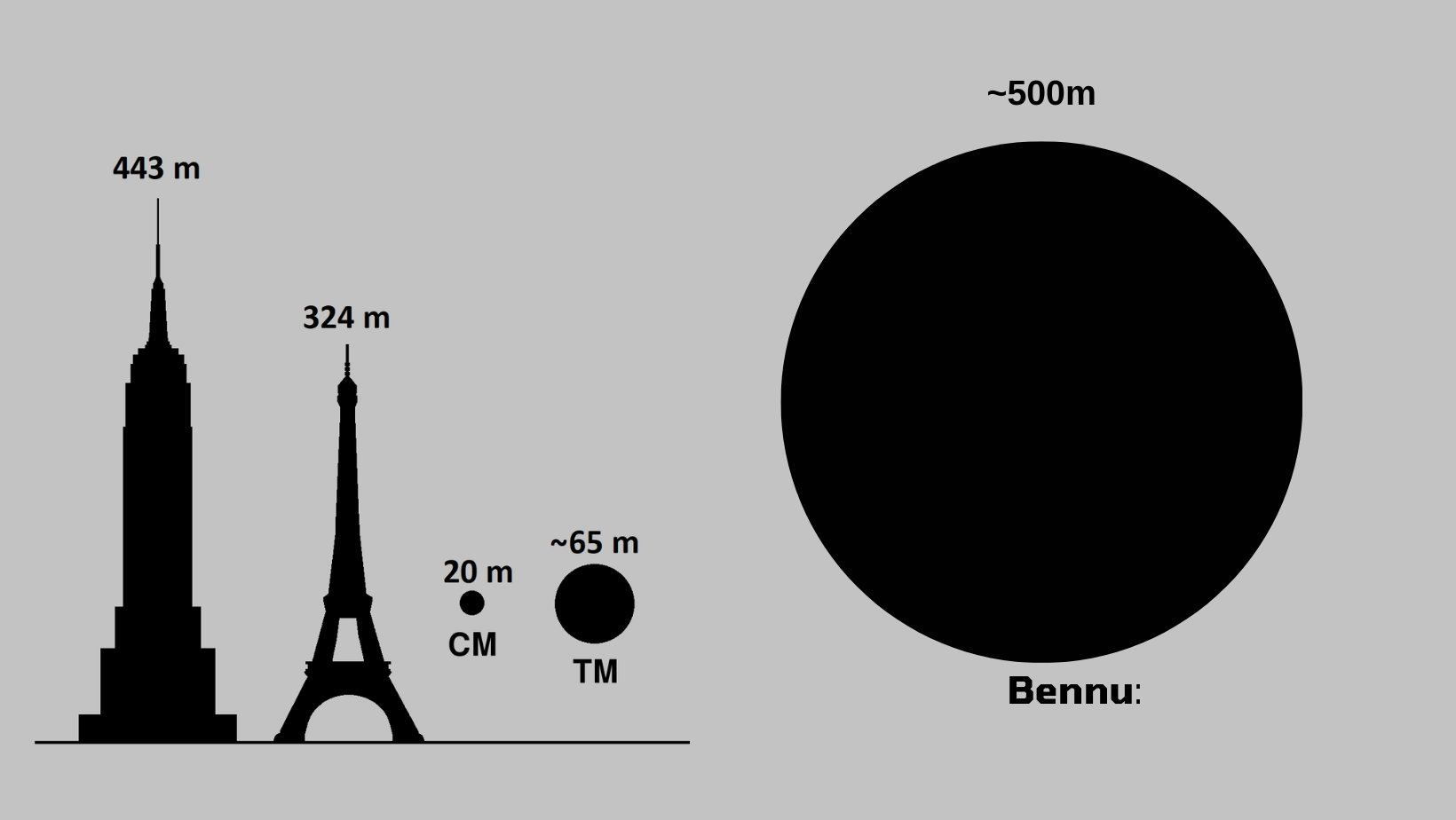
How big is the planet killer asteroid?
The term “planet killer” refers to any asteroid larger than 1 kilometer. With a diameter ranging from 1.1 km to 2.3 km, asteroid 2022 AP7 is the biggest potentially harmful asteroid (PHA) discovered in the past eight years. The effect of such an object, which would throw dust and contaminants into the atmosphere, would be disastrous to life as we know it and would last for years.
Can a planet killer hit Earth?
There is “tiny probability” that such an occurrence will occur in the near future. Although extremely unlikely, it is not completely impossible for such a catastrophic event to occur. To understand the risks, we must study the science and safety measures of asteroid strikes.
How would NASA stop an asteroid?
Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) are first and mainly found and tracked by NASA using a vast network of ground-based telescopes. They can predict any hazards in advance and accurately determine their course by constantly scanning the skies. The Planetary Defence Coordination Office (PDCO) of NASA takes action when an asteroid is recognised as posing a threat. Global partners aid in gathering important information about the asteroid. The outcomes of an impact are then predicted by NASA using computer simulations and models. This aids them in choosing the most effective strategy for destroying or diverting the asteroid.


Leave a Reply