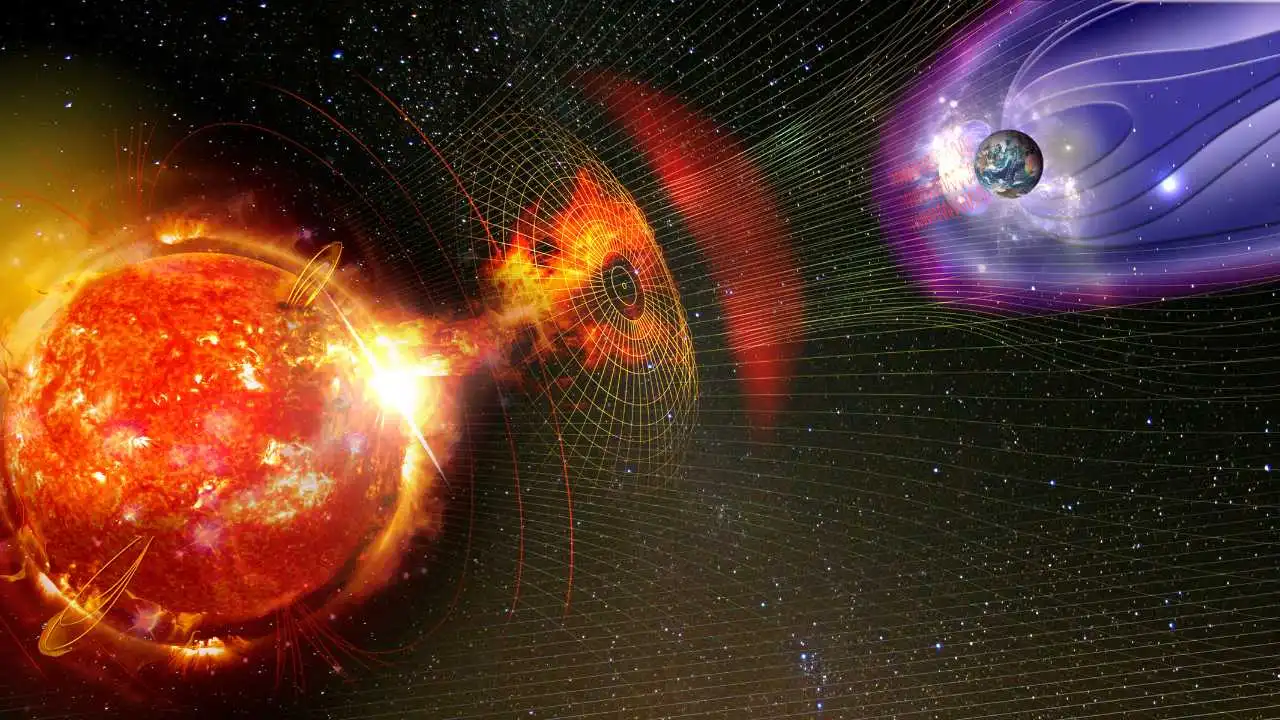
The sun is a glowing ball of gasses at the centre of our solar system. It is made of a gas-like material called plasma, consisting of charged particles. The sun not only provides the energy necessary for life on Earth but also generates a powerful and complex magnetic field.
This magnetic field affects many solar phenomena, such as coronal mass ejections, sunspots, and solar flares. The sun’s magnetic field comes from the flow of charged ions and electrons. It extends 18.5 billion km through a region called the heliosphere, the outermost boundary of our solar system. For a better understanding of the origin of the sun’s magnetic field, it is essential to look into the detailed processes occurring within its interior.
Origin of the sun’s magnetic field
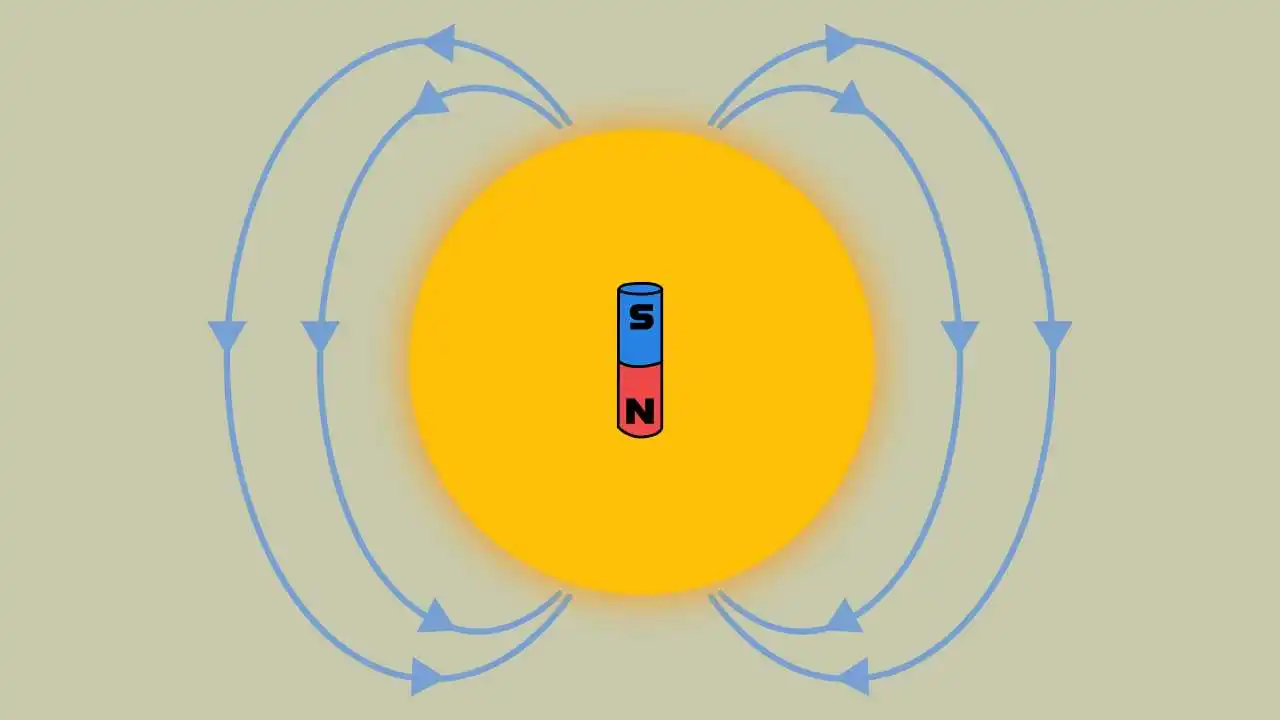
The process of production of magnetic fields in the sun is known as solar dynamo. It is a mechanism in which the kinetic energy from the sun’s rotating plasma is converted into magnetic energy.
This generation process of the sun’s magnetic field occurs in the solar convection zone, a layer extending from approximately 70% of the sun’s radius just beneath its surface. Hence, the magnetic field of the sun comes from the outer layers of it rather than from deep layers unlike the stars as scientists thought before.
Also read: Can the Sun Become a Black Hole?
New studies suggest that the sun’s magnetic field may be produced near the surface of the sun. An international team of scientists and mathematicians including Lecoanet and Vasil discovered that the magnetic field of the sun is produced (20,000 miles) 32,200km beneath the surface of the sun. Some previous theories suggested that the magnetic field produced about 209,000km below the surface.
A co-author from Northwestern University suggested that the magnetic field is generated deep in the sun. He further added:
You can think of the magnetic field as a rubber band and the motion near the top of the sun is pulling in that rubber band until it gets so extended that it breaks and when it breaks, then launches the material from the sun out into space.
How is the sun’s magnetic field created?
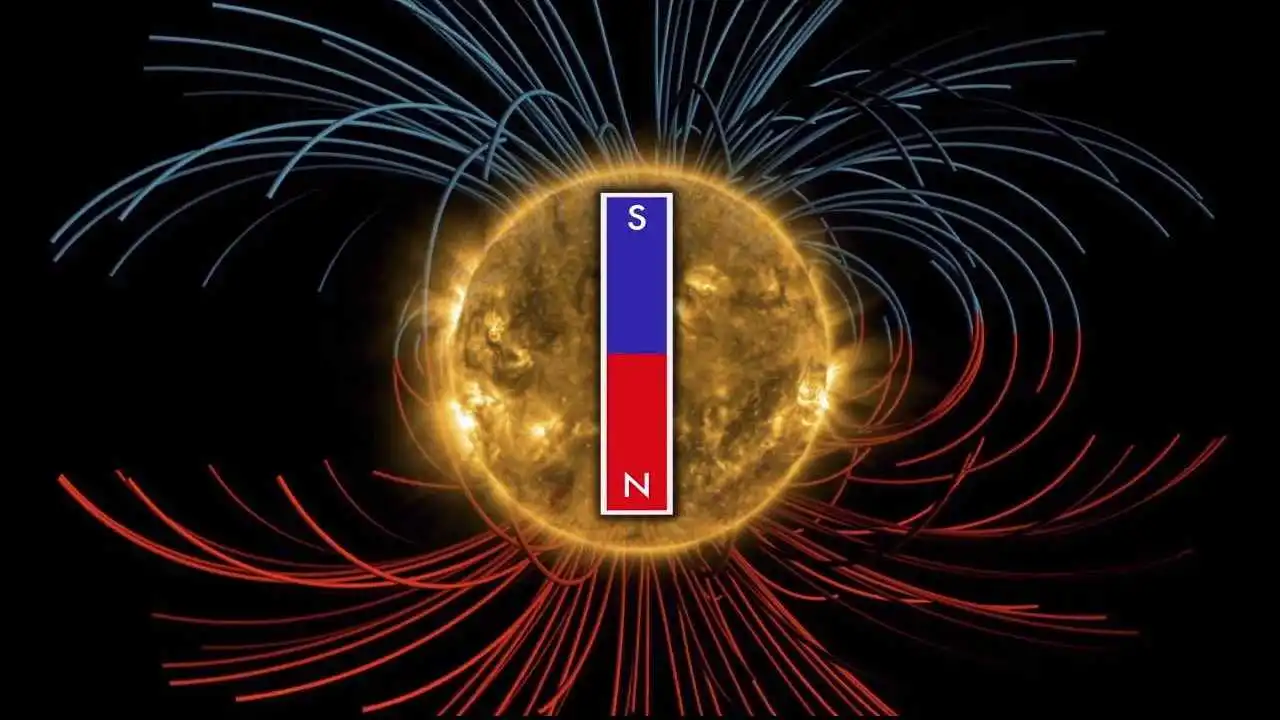
The complex interaction of plasma flows within the convection and tachocline zone of the sun gives rise to the sun’s magnetic field. In the interior of the sun, there is an interplay of convective motions, rotations, stretching, and tangling magnetic field lines, thus generating and amplifying the magnetic field.
🔬 Subscribe to SciMail
Get the latest science discoveries straight to your inbox!
Appearance of the sun’s magnetic field
The magnetic field lines appear from the surface of the sun creating dark patches on the surface called sunspots. Sunspots are the points where the magnetic field of the sun is stronger than the Earth’s about 2,500 times. Sunspots are very specks on the surface of the sun as compared to the sun’s massive body.
There are almost 200 sunspots at a time on the sun. Magnetic fields can’t cross each other but sometimes knot, resulting in bursts of radiation called solar flares or the vast amounts of plumes of solar material known as coronal mass ejections.
The first astronomer to study sunspots was Galileoin in the early 1600s. Solar flares and coronal mass ejections occur near the sunspots and the dark patches are gigantic as the earth is located close to the intense portions of the sun’s magnetic field.
Why is the sun’s magnetic field tangled?
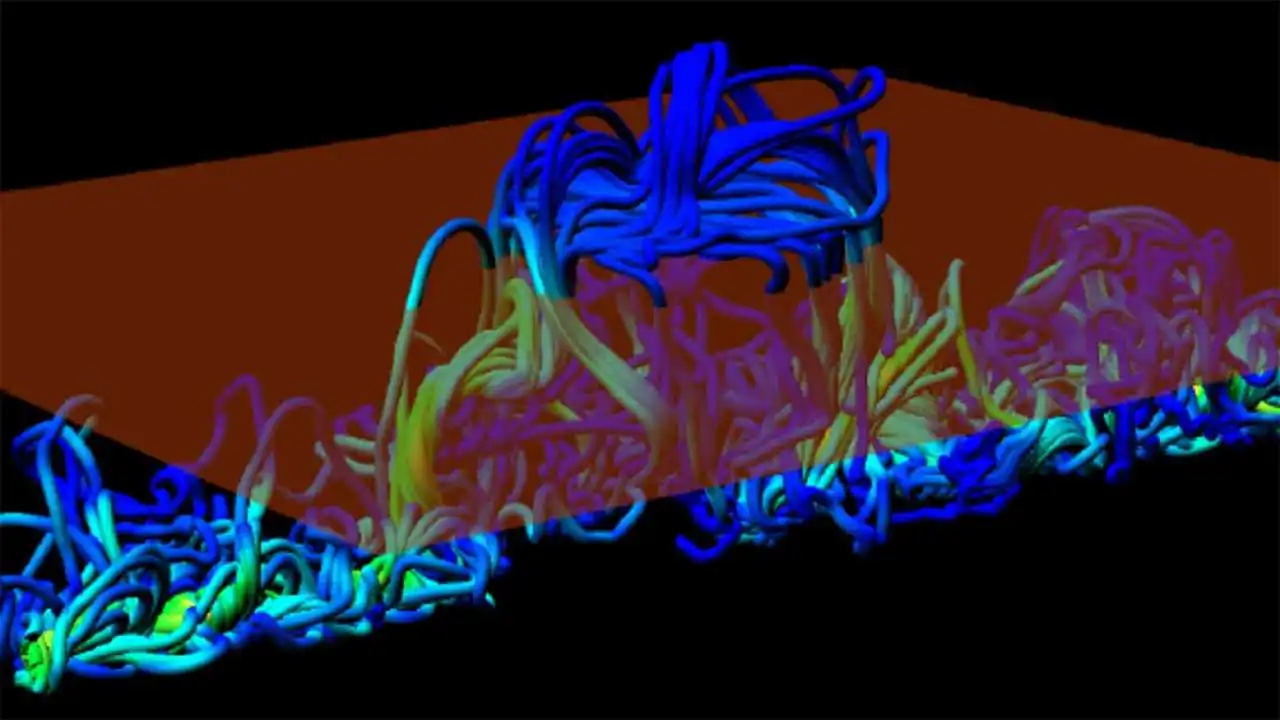
Convective motion and Rotation stretch and curl the magnetic field lines, thus producing and amplifying the magnetic field through alpha and omega effects. Convective motion occurs within the convection zone and contributes to the production of the sun’s magnetic field through the alpha effect.
While the rotation of the sun causes a continuous rise and fall of hot plasma which creates helical motion. The magnetic field lines tangle due to these helical motions converting run north-south fields into run east-west fields and vice versa.
Is the magnetic field of the sun constant?
The sun’s magnetic field moves along a cycle called the solar cycle. After every 11 years, the magnetic field changes completely. Because the South and North poles of the sun switch their positions. It happens when the sun reorganizes its inner magnetic dynamo. The field of the sun varies every 11 years besides the location of the poles.
Why is the sun’s magnetic field important?
The sun’s magnetic field predicts the space weather. The magnetic field lines are the links between sunspots. When these lines twist, they show the chances of solar flares. The magnetic field protects our planet from cosmic rays and the charged particles, generated by the motion of molten iron in the Earth’s core.
Also Read:
When will the sun die?
How many earths can fit into the sun?


Leave a Reply